Figure 5.
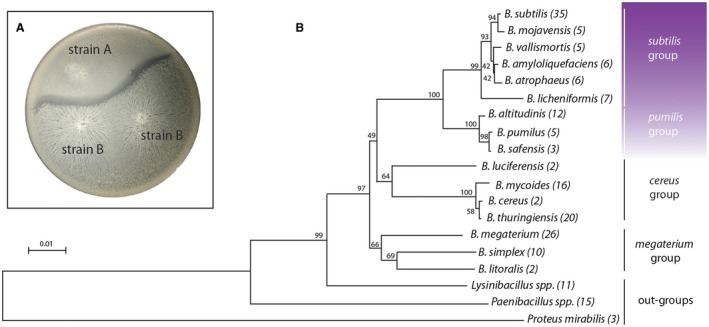
Kin discrimination in B. subtilis. A. Different phenotypes of approaching B. subtilis swarms can be used to distinguish kin and non‐kin strains of B. subtilis. Merging swarms indicate kin (two B strains) and a striking boundary indicates non‐kin swarms (strain A and strain B) (Stefanic et al., 2015); B. Phylogenetic tree adapted from Lyons and Kolter, 2017. The tree was calculated using the 16S rRNA sequence of a reference strain of each indicated species. The number of isolates of each species used in the study is indicated in parentheses. The separate clades are marked beside the tree and the purple gradient represents the cut‐off point for kin discrimination against Bacillus subtilis NCIB 3610.
