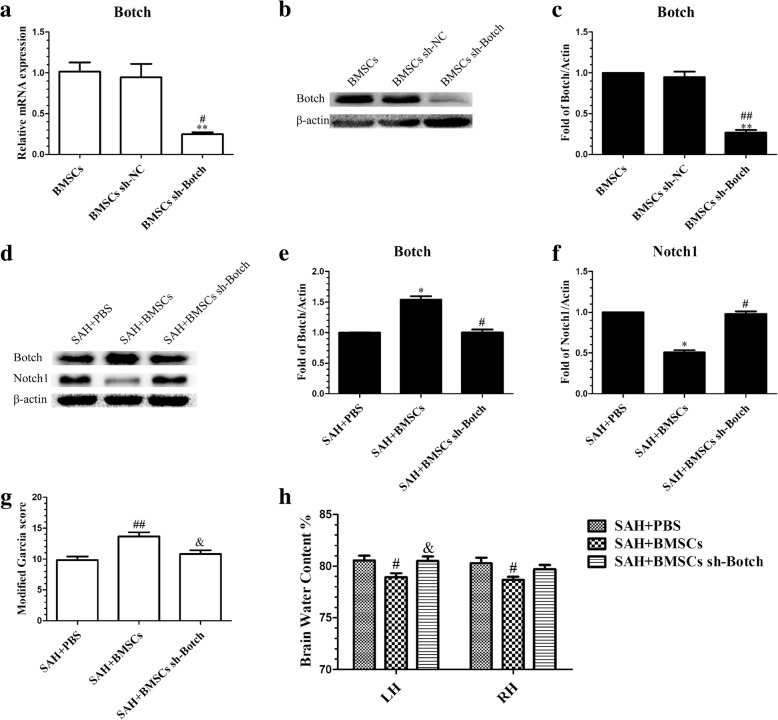
Fig. 11.
Botch shRNA-mediated knockdown of Botch in BMSCs abolished their protection of EBI after SAH. The efficiency of shRNA-mediated knockdown of Botch in BMSCs was confirmed by qRT-PCR (a) (n = 3/group) and Western blotting (b) (n = 6/group). Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01 versus BMSCs group, #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01versus BMSCs sh-NC group (c). Representative images of Western blot data showing the expression of Botch and Notch1 in SAH + PBS, SAH + BMSCs, and SAH + BMSCs sh-Botch groups (d). Quantitative analyses of Botch (e) and Notch1 (f) expression indicating that BMSCs sh-Botch transplantation significantly decreased Botch expression in brain tissue at 24 h post-SAH but increased Notch1 expression; n = 6 in each group; data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus SAH + PBS group, #P < 0.05 versus SAH + BMSCs group. BMSCs sh-Botch treatment accelerated neurobehavioral deficits (g) and BWC (h) compared with BMSCs treatment group; n = 6 in each group; data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus SAH + PBS group, &P < 0.05 versus SAH + BMSCs group