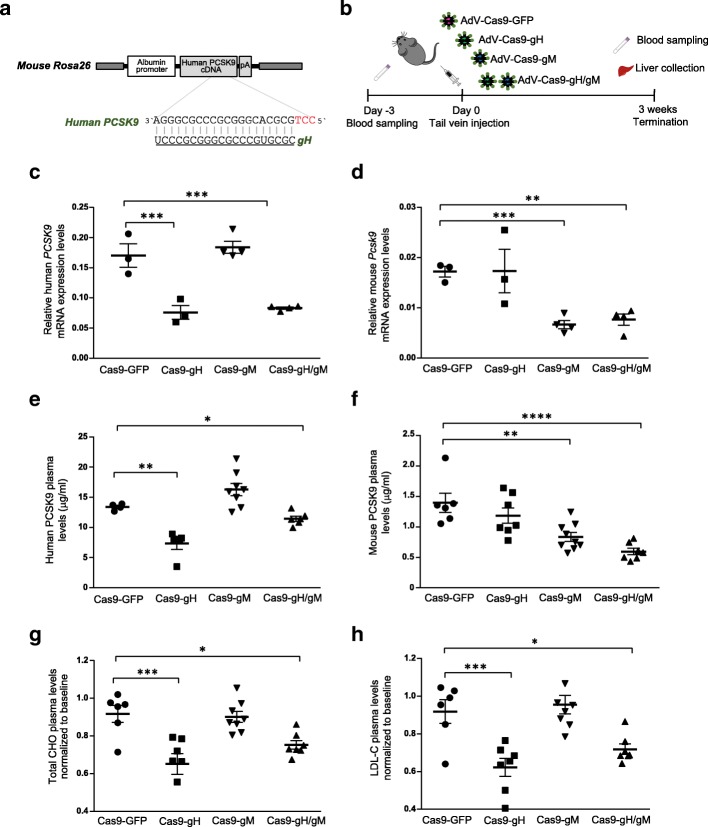
Fig. 2.
Cas9-mediated in vivo knock-out of human PCSK9 and mouse Pcsk9 in hPCSK9-KI mice. a Targeted region at human PCSK9 locus. The guide RNA gH targets the human PCSK9 cDNA knocked into the mouse R26 locus. b Experimental design: 28-week-old hPCSK9-KI mice were transduced with adenoviral vectors (AdV) encoding Cas9 together with gH, gM (targeting mouse Pcsk9), both gH and gM (gH/gM), or GFP as control. Blood was collected 3 days before injection (baseline); the blood and liver were collected 3 weeks after injection. c, d Human PCSK9 and mouse mPcsk9 mRNA expression levels relative to β-actin in the liver from mice 3 weeks after Cas9 treatment (n = 3 for the Cas9-GFP and Cas9-gH groups and n = 4 for the Cas9-gM and Cas9gH/gM groups). e, f Plasma concentrations of human and mouse PCSK9 proteins 3 weeks after Cas9 treatment (n = 6 for the Cas9-GFP group; n = 7 for the Cas9-gH and Cas9gH/gM groups; n = 8 for the Cas9-gM group). g, h Plasma concentrations of total cholesterol (CHO) and LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) 3 weeks after Cas9 treatment (normalized to plasma concentrations at baseline; n = 6 for the Cas9-GFP group; n = 7 for the Cas9-gH and Cas9gH/gM groups; n = 8 for the Cas9-gM group). Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s correction for multiple testing. Values are presented as group means ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001