Figure 3.
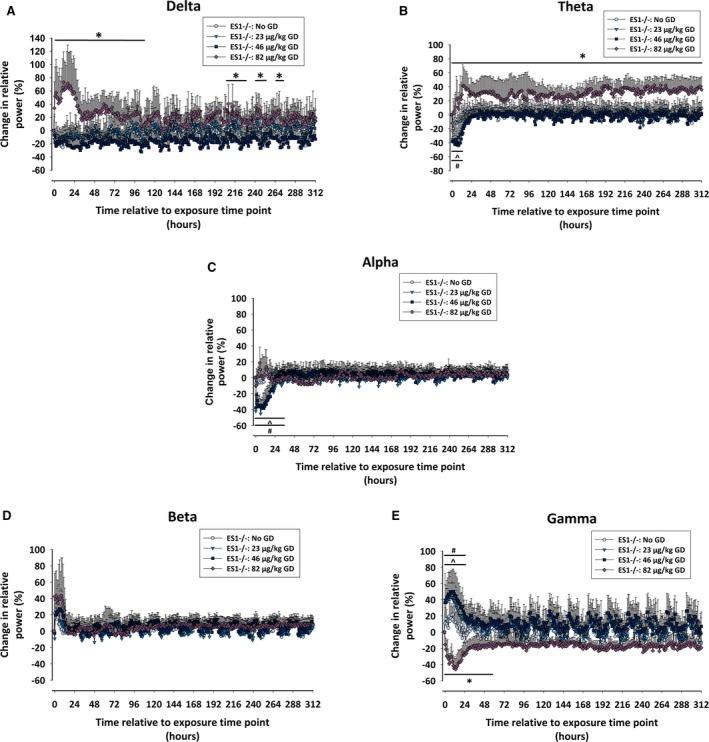
Effects of GD exposure on electroencephalography (EEG) power spectra of male ES1−/− mice. The percent of relative change from baseline in the power of (A) delta (0.1‐4 Hz), (B) theta (4.1‐8 Hz), (C) alpha (8.1‐12 Hz), (D) beta (12.1‐25 Hz), and (E) gamma (25.1‐50 Hz) EEG frequencies was calculated for ES1−/− mice exposed to GD and administered delayed midazolam treatment. Effect of GD exposure on individual power spectra throughout the duration of the study was determined by 2‐way ANOVA analysis, and the change in relative power for mice exposed to 23, 46, and 82 μg/kg GD were compared to values of control (No GD) animals. In ES1−/− mice exposed to 82 μg/kg GD the oscillations in gamma and beta power intensity that coincide with sleep/wake cycles disappear in comparison with the other mouse groups. Statistically significant differences between groups at particular time points are marked by a line drawn above or below the graphed data *P < 0.05, 82 μg/kg GD compared to No GD; ^P < 0.05; 46 μg/kg GD compared to No GD; #P < 0.05, 23 μg/kg GD compared to No GD
