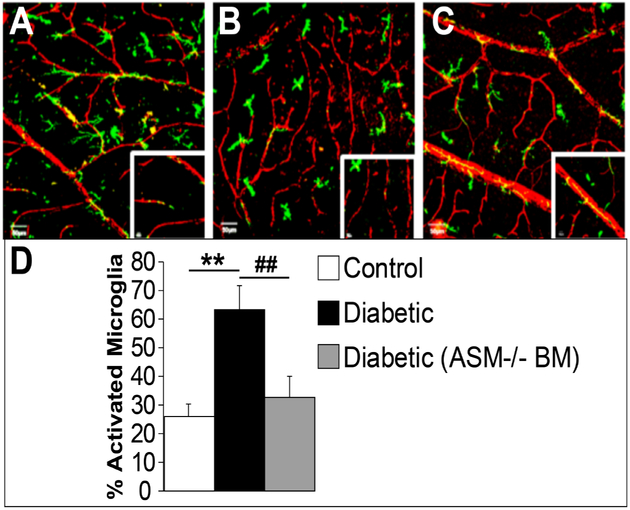
Figure 5: BM-ASM inhibition prevents activation of microglia in diabetic retinas.
Confocal images of retinal flat mounts from bone marrow chimeras with GFP (green), or GFP-ASM−/− bone marrow donors and wild type recipient mice. The retinas are stained with collagen IV for the retinal vasculature (red). (A) Control retina showing resting microglia with the typical ramified and branching shape. (B) Diabetic animals show activated microglia with more compact cells with fewer ramifications. (C) Diabetic animal showing that BM-ASM inhibition prevents activation of microglia. (D) Bar chart showing the quantification of the percentage of activated microglia in the three conditions. Scale bar is 50 μM, n=8