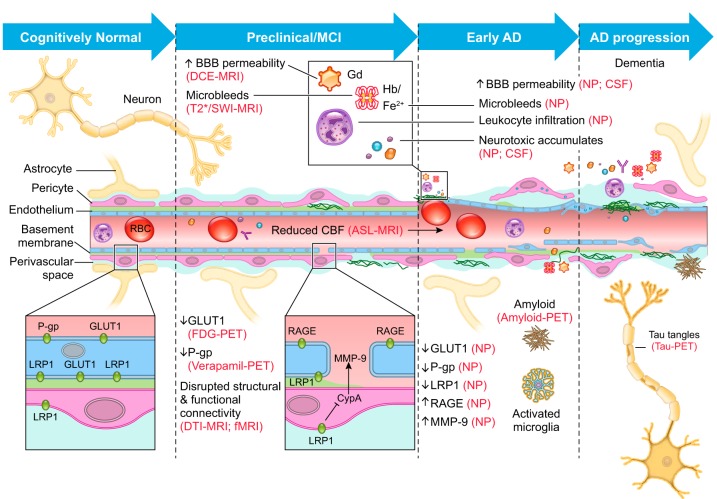
FIGURE 7.
Blood-brain barrier breakdown and dysfunction in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) has shown blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown in the hippocampus in individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and in different gray and white matter regions in early Alzheimer’s disease (AD), before brain atrophy and dementia occur. Microbleeds reflecting loss of cerebrovascular integrity and BBB breakdown have been shown by T2*-MRI and susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)-MRI during MCI stage, which progresses and augments through early stages of AD. Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) has indicated diminished BBB GLUT1 transporter activity mediating glucose uptake by the brain before brain atrophy, dementia, or amyloid-β (Aβ) pathology. Similarly, diminished active efflux ABCB1 (P-gp) BBB transporter activity was shown by verapamil-PET in early AD. Early BBB breakdown and vascular dysfunction in MCI and AD has been confirmed by some studies by elevated levels of vascular biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood before Aβ and tau pathology, and dementia. Neuropathological (NP) analysis of mild and advanced AD cases confirmed accumulation of perivascular blood-derived deposits including, to name a few, fibrin(ogen), thrombin, red blood cells (RBC)-derived iron-containing products that all are potentially toxic for the neural tissue. In addition, pericyte degeneration, endothelial degeneration, and brain infiltration with circulating macrophages and neutrophils were associated with BBB breakdown of AD cases on NP analysis. Diminished expression levels of BBB GLUT1 and ABCB1 (P-gp) transporters have been shown by post mortem NP analysis of AD cases, as well as downregulation of Aβ BBB clearance receptors LRP1 and ABCB1, suggesting impaired Aβ clearance. Furthermore, APOE4 carriers develop accelerated BBB breakdown associated with activation of proinflammatory cyclophilin A (CypA)-matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) pathway at the BBB, which degrades endothelial tight junction and basement membrane proteins enhancing BBB damage. How changes in BBB permeability as measured by advanced neuroimaging techniques in the living human brain relate to disrupted structural and functional connectivity as measured by diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI)-MRI and functional MRI (fMRI), and amyloid-PET and tau-PET findings remains unclear at present.