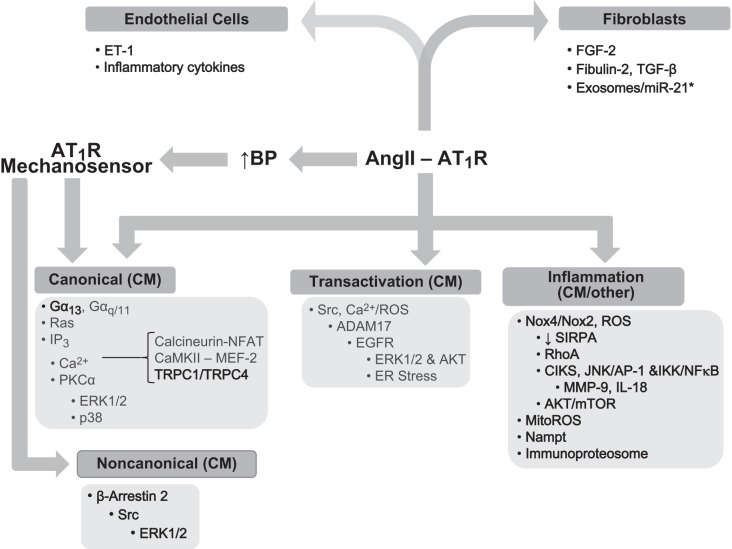
FIGURE 8.
ANG II induces cardiac hypertrophy by multiple means involving direct actions on cardiac myocytes (cm) or the release of paracrine factors from other cell types, such as endothelial cells and fibroblasts/myofibroblasts. Developments within the last 5 yr are noted in darker text and are highlighted here. Three processes are dominant in cardiac myocytes: canonical signaling, transactivation of EGFR, and inflammatory signaling. The later may involve other cell types as the source of ROS. For canonical signaling, Gα13 was recently shown to regulate RhoA activation that was linked to activation of myocardin-related transcription factors. A background Ca2+ entry pathway formed by TRPC1 and TRPC4 channels was also implicated in ANG II-induced cardiac hypertrophy via canonical means. AT1R may couple to cardiac hypertrophy as a mechanosensor for increased blood pressure (BP) via β-arrestin 2 biased signaling that involves activation of Src and ERK1/2. As a mechanosensor, AT1R may conceivably activate canonical signaling as well. Inflammation is driven by Nox4- and Nox2-derived ROS that leads to the engagement of a number of processes that sustain hypertrophic signaling, such as the downregulation of the TLR4 inhibitor, SIRPA, as well as the activation of RhoA and Akt/mTOR signaling. Mitochondria are an additional source of ROS for cardiac hypertrophy (MitoROS). The adaptor molecule CIKS may couple AT1R to cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, downstream of Nox2 activation. ANG II enhances expression and activation of CIKS in cardiac myocytes leading to IKK/NF-κB and JNK/AP-1 activation and subsequent induction of MMP-9 and IL-18, a growth factor for cardiac myocytes. Secreted Nampt from cardiac myocytes, as well as the generation and activation of the immunoproteasome, may also contribute to ANG II-induced cardiac hypertrophy. In response to ANG II, endothelial cells release ET-1 and inflammatory cytokines that induce cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Activated fibroblasts stimulate hypertrophy by releasing FGF-2, fibulin-2, TGF-β, and exosomes that are enriched in passenger strand miR-21*.