Figure 3.
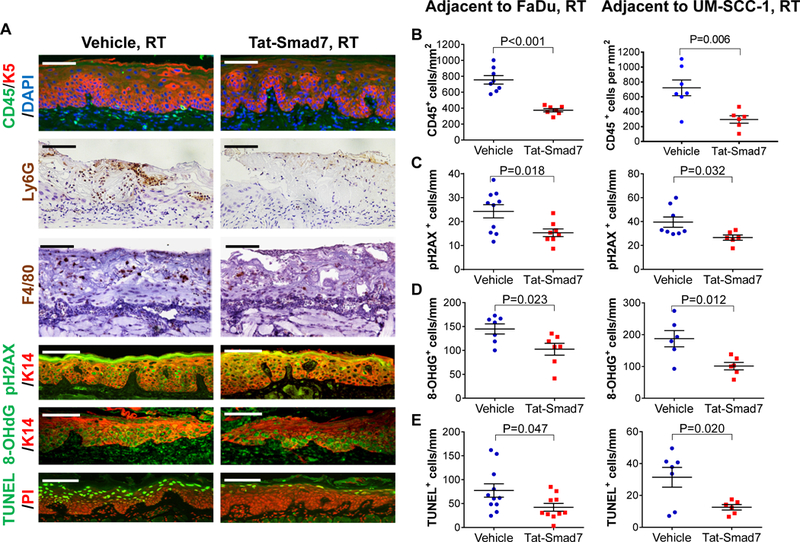
Oral Tat-Smad7 treatment mitigated inflammation, DNA damage and apoptosis in RT-induced oral mucositis. (A) Representative immunostaining of markers for immune cells (CD45, Ly6G, F4/80), DNA damage markers (pH2AX, 8-OHdG) and apoptosis (TUNEL) in RT+Vehicle or RT+Tat-Smad7 treated oral mucosa adjacent to irradiated FaDu tongue tumors. Similar staining patterns were also seen in irradiated mucosa adjacent to UM-SCC-1 tumors (not shown) and quantified in B-E. K5 or K14 antibody was used to counterstain epithelial cells. DAPI was used to counterstain nuclei for CD45 staining, propidium iodide (PI) was used to counterstain nuclei for TUNEL. Scale bars = 100 μm for all sections. (B-E): Quantification (mean ± SEM) of immunostaining markers in oral mucosa adjacent to irradiated FaDu and UM-SCC-1 shown in (A). CD45+ cells (B) were quantified based on mm2 epithelial and stromal areas above the muscle layer. Quantifications for pH2AX+ cells (C), 8-OHdG+ cells (D) and TUNEL+ cells (E) in keratinocytes per mm basement membrane length. P values were determined by Student’s t test.
