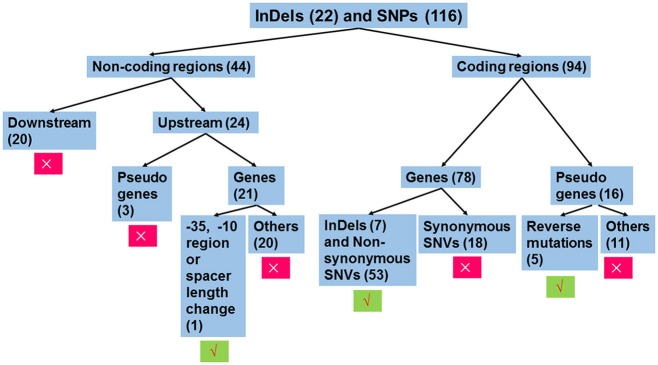
Figure 1.
Workflow of sequence analysis to predict the effect of mutations on gene functions. Variations that affect the transcription of gene(s) or amino sequences were thought to be functional mutations. Otherwise, these were treated as silent mutations. Insertions or deletions (InDels) and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in non-coding regions and coding regions were separately treated. For mutations in non-coding regions, only those mutations that changed the −35 hexamer, −10 hexamer, or their spacing length were further analyzed, since these mutations potentially affect promoter strength. For variations in coding regions, mutations leading to changes in amino acid sequences were analyzed, including functional ORFs with InDels or non-synonymous substitutions and pseudo genes with function restoration. The number in the parenthesis indicates the number of mutations belonging to the group. Symbols × and √ indicate exclusion and inclusion for further analysis, respectively.