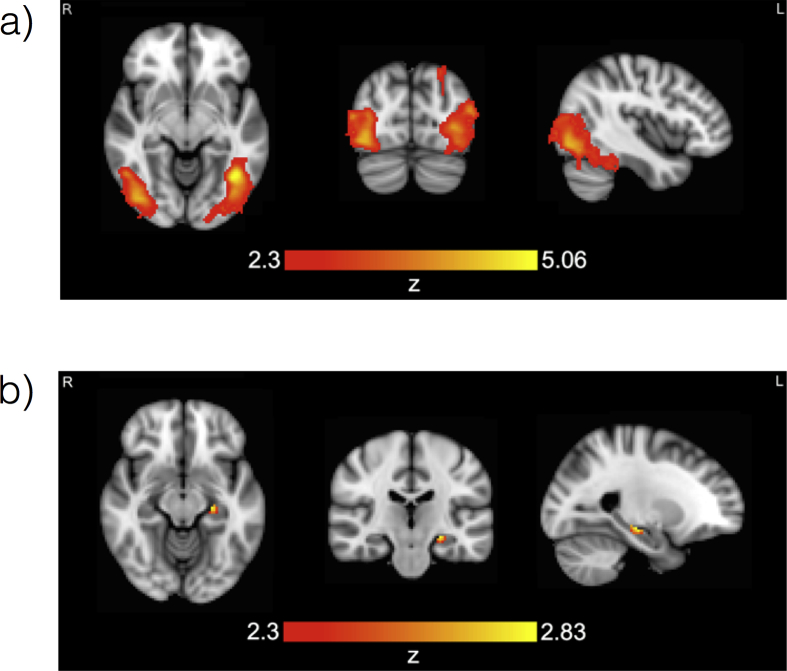
Fig. 2.
Group average results for remembered versus forgotten. (a) Whole brain analysis: the brain areas that were significantly more active for subsequently remembered stimuli than for subsequently forgotten stimuli. These are bilateral occipitotemporal regions. They include the lateral occipital cortex, the occipital pole, the occipital fusiform gyrus, the temporo-occipital part of the inferior temporal gyrus and the temporal occipital fusiform cortex bilaterally, in addition to part of the posterior temporal fusiform cortex and the posterior parahippocampal gyrus in the right hemisphere. The maxima can be viewed in Table 3. (b) Left hippocampus region of interest analysis: a region in the left hippocampus that was more active for subsequently remembered stimuli than for subsequently forgotten stimuli. The peak voxel is found at −24, −22, −12 (MNI coordinates, mm), Z = 2.83.