Figure 2.
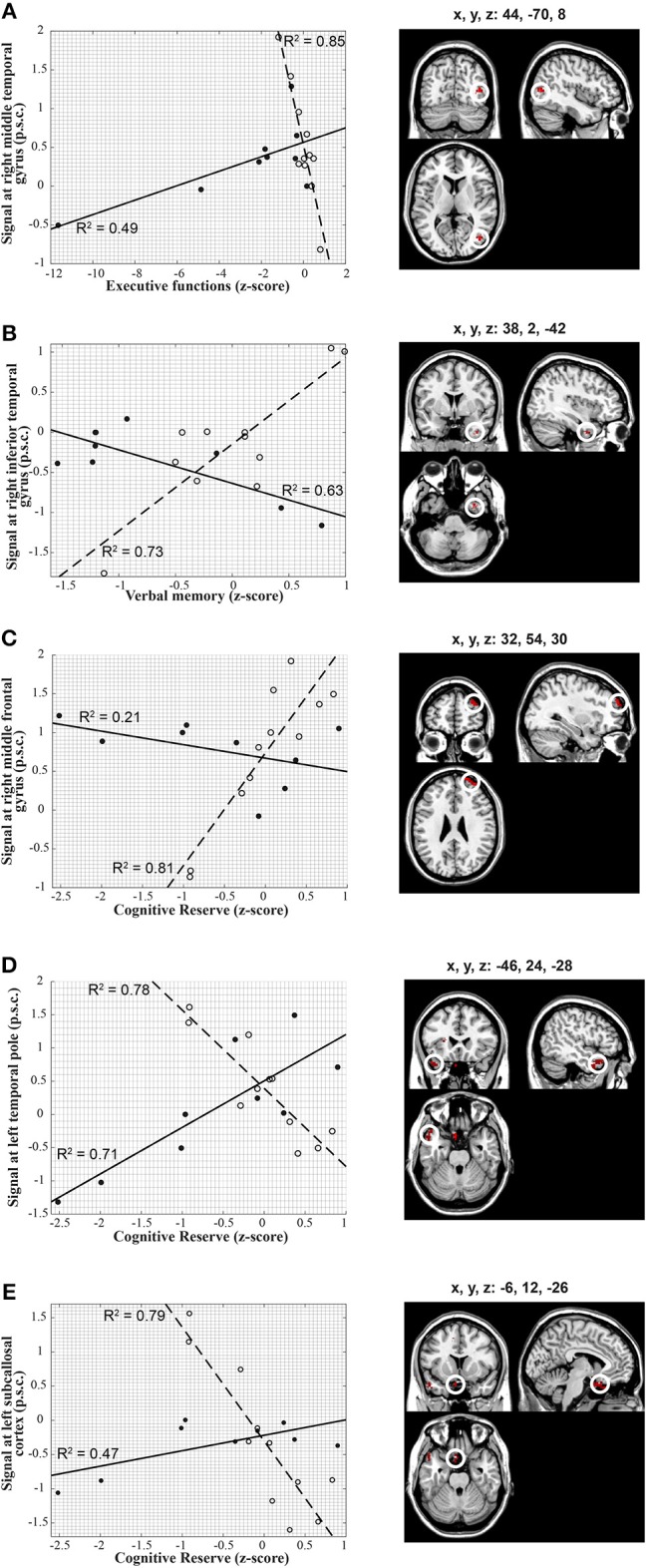
Voxel-wise correlations between ICC extracted from brain regions depicted on the right-hand panels and individual scores in the cognitive constructed measures along with the corresponding scatter plots (left-hand panels). The scatter plots on the left show in detail the relationship between ICC and cognitive measures in each of the statistical peaks for both groups (TBI: solid lines, closed circles, HC: dashed lines, open circles). Results are overlaid onto a standard single subject T1-weighted MR-image (ch2-template) in the MRICroN software (71). (A) Correlation between the cognitive measure of executive function and right middle Temporal gyrus in both groups. The correlation of ICC with executive function scores was positive in participants with TBI [r(6) = 0.70; p = 0.04] and negative in the healthy controls [r(9) = −0.92; p < 0.001] for the right middle temporal gyrus [peak at x, y, z = 44, −70, 8; t(1, 16) = 6.66; p-FDR < 0.05]. (B) Correlation between verbal memory and right inferior Temporal gyrus in both groups. The correlation of ICC with verbal memory scores was negative in participants with TBI [r(6) = 0.79; p = 0.01] and positive in the healthy controls [r(9) = 0.85; p = 0.001] for the right inferior Temporal gyrus [peak at x, y, z = 38, 2, −42; t(1, 16) = 6.01; p-FDR = 0.04]. (C) Correlation between cognitive reserve and right middle Frontal gyrus in both groups. The correlation of ICC with cognitive reserve scores exhibited a negative trend in participants with TBI but did not reach statistical significance [r(6) = −0.46; p = 0.21], whereas it was positive in the healthy controls [r(9) = 0.90; p < 0.001] for the right middle frontal gyrus [peak at x, y, z = 32, 54, 30; t(1, 16) = 6.13; p-FDR < 0.001]. (D) Correlation between cognitive reserve and left Temporal pole in both groups. The correlation of ICC with cognitive reserve scores was positive in participants with TBI [r(6) = 0.84; p = 0.005] and negative in the healthy controls [r(9) = −0.88; p < 0.001) for the left temporal pole [peak at x, y, z = −46, 24, −28; t(1, 16) = 6.46; p-FDR < 0.001). (E) Correlation between cognitive reserve and left Subcallosal cortex in both groups. The correlation of ICC with cognitive reserve scores was positive in participants with TBI [r(6) = 0.68; p < 0.05] and negative in the healthy controls [r(9) = −0.89; p < 0.001] for the left subcallosal cortex [peak at x, y, z = −6, 12, −26; t(1, 16) = 6.80; p-FDR < 0.001]. Percent signal change, p.s.c.
