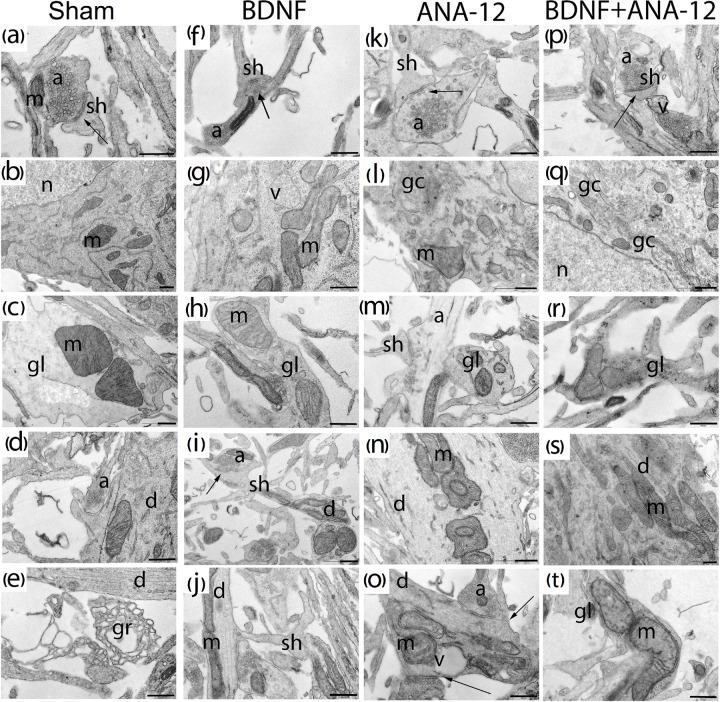
FIGURE 7.
Representative electron microscopy images of dissociated hippocampal cells on DIV 10. (a–e) Sham, (f–j) BDNF, (k–o) ANA-12, (p–t) BDNF + ANA-12. (a) Axo-spiny synapse; the cristae of mitochondria in a dendrite are smooth. (b) Neuronal soma; the cytoplasm shows well-visualized mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, granular endoplasmic reticulum, and numerous free ribosomes. (c) Mitochondria in a glial cell; cristae are smooth, and the glia-glial gap junction is well visualized. (d) Cisterns of the endoplasmic reticulum in a dendrite are expanded, and the cristae in a mitochondrion are smooth. (e) Growth cone. (f) Mitochondrion in a neuronal axon. (g) Mitochondria in a neuronal soma, some are without cristae and have an enlightened matrix, a vacuole, and numerous free ribosomes. (h) Glial outgrowth, a few glycogen pellets and uneven cristae in a mitochondrion are visible. (i) Axo-spiny contact; mitochondria in a dendrite have swollen cristae. (j) Dendritic spine. (k) Axo-spiny synapse, short postsynaptic density (PSD), few synaptic vesicles near the active zone, and large osmiophilic bubbles in an axon. (l) Part of the cell body; a destroyed Golgi apparatus is visualized, mitochondria have normal structures, and an extremely low number of ribosomes are present on the endoplasmic reticulum. (m) Mitochondria in a glial cell, axonal outgrowth, and an enlightened axoplasm. (n) Mitochondria in a dendrite are densely packaged, have an irregular shape and exhibit cristae with small extensions. (o) Axo-dendritic synapse, destroyed mitochondria in a dendrite. (p) Mature axo-spiny synapse, a vacuole in an axon. (q) Increased Golgi apparatus area, a vacuole and destroyed mitochondria in the cytoplasm. (r) Mitochondria with impaired internal structures in a glial outgrowth, with a large number of osmiophilic bubbles. (s) Mitochondria in a large dendrite. (t) Mitochondria in a glial outgrowth have impaired internal structures. Scale bar – 0.5 μm.