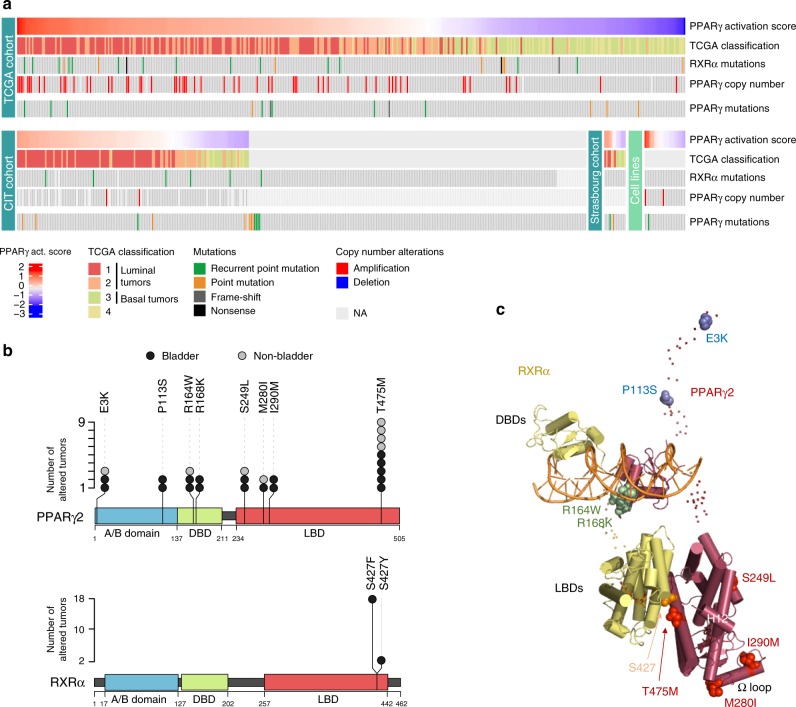
Fig. 1.
Mutations of PPARγ and RXRα in bladder tumors. a Oncoprints of PPARγ and RXRα mutations in three series of bladder tumors and a panel of 25 bladder tumor cell lines. Samples were sorted by PPARγ activation score when transcriptomic data were available. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. b Lolliplot representations of recurrent mutations of PPARγ (upper panel) and RXRα (lower panel) identified in the 859 bladder tumors studied here (black circles) or in publicly available data available for other bladder tumors and other types of cancer from the COSMIC and cBioPortal databases (Supplementary Table 4) (gray circles). Sequences are numbered according to the PPARγ2 isoform. A/B: N-terminal domain; DBD: DNA-binding domain; LBD: ligand-binding domain (LBD). c Position of the residues affected by the recurrent PPARγ and RXRα mutations on the full-length PPARγ-RXRα-DNA-coactivator peptide solution structure51. The folded domains are shown in cartoon representation and the disordered hinges and NTDs are shown as dots. The mutated residues are shown as spheres. The residues mutated in PPARγ are colored in blue (A/B domain), green (DBD), and red (LBD). The residue mutated in RXRα is colored in orange. Source data are provided as a Source Data file