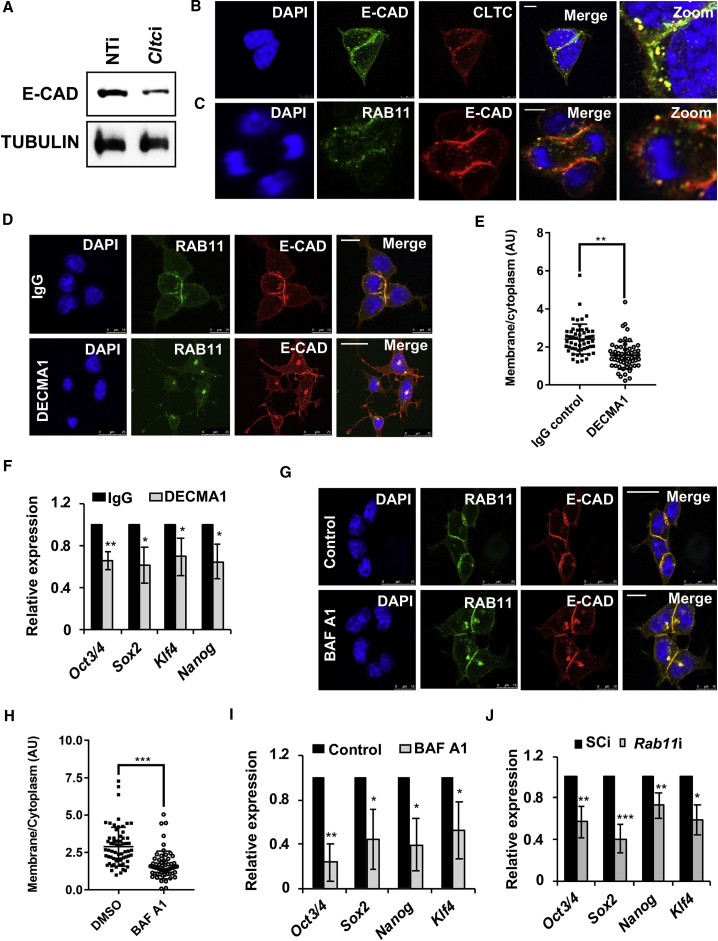
Figure 2.
E-CAD Trafficking Is Required to Maintain mESC Pluripotency
(A) Western blot showing E-CAD levels upon knockdown of Cltc in mESCs.
(B and C) Representative confocal micrographs showing the co-localization of E-CAD with CLTC (B) and RAB11 (C). Scale bars, 7.5 μm (B) and 10 μm (C).
(D) Representative confocal micrographs showing the increased localization of E-CAD with RAB11-positive recycling endosomes in the presence of the E-CAD neutralizing antibody, DECMA1 (1 hr treatment). Scale bars, 10 μm (top panel) and 25 μm (lower panel). Mouse IgG was used as a control.
(E) Scatterplot showing the quantitation of E-CAD levels, membrane versus cytoplasmic, in the presence of the E-CAD neutralizing antibody, DECMA1. ∗∗p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student’s t test.
(F) Graph showing levels of pluripotency marker genes by qRT-PCR analysis in mESCs treated with the E-CAD neutralizing antibody, DECMA1 or mouse IgG (24 hr treatment). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student’s t test.
(G) Representative confocal micrographs showing E-CAD accumulation in RAB11-positive endosomes in mESCs treated with BAF-A1. DMSO was used as a vehicle control. Scale bars, 25 μm (top panel) and 10 μm (lower panel).
(H) Scatterplot showing the quantitation of E-CAD levels, membrane versus cytoplasmic; in mESCs treated with BAF-A1. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test.
(I) Graph showing levels of pluripotency marker genes by qRT-PCR analysis in mESCs treated with BAF-A1 or DMSO.
(J) Graph showing levels of pluripotency marker genes by qRT-PCR analysis upon Rab11 knockdown in mESCs. SCi, scrambled shRNA control; Rab11i, Rab11 shRNA.
Error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t test.