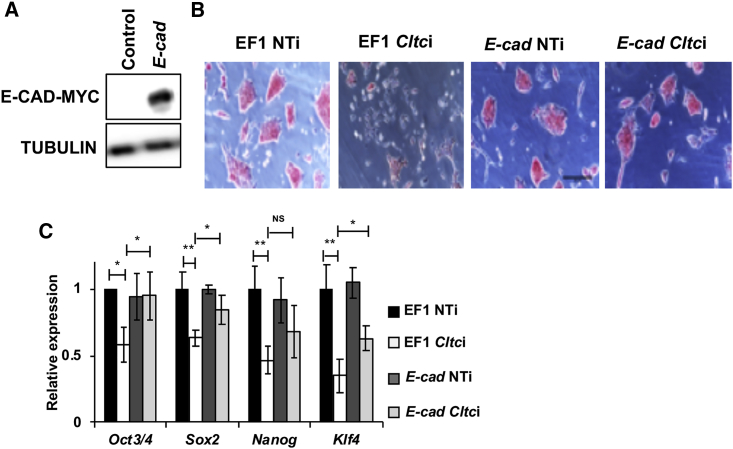
Figure 5.
Effect of Cltc Knockdown in mESCs Can Be Partially Rescued by Overexpressing E-cad
(A) Western blot showing the overexpression of E-CAD in mESCs post transfection with the pEF1-E-cad vector. The EF1 empty vector is used as a control.
(B) Representative micrographs showing the morphology of mESCs in the presence of empty vector (EF1), and vector-expressing E-cad (pEF1-E-cad) in combination with either NTi or Cltci. Scale bar 50 μm.
(C) Bar graph showing the levels of pluripotency marker genes in the presence of the empty vector or upon E-cad overexpression. EF1, empty vector; E-cad, EF1-E-cad vector; NTi, non-targeting siRNA control; Cltci, Cltc siRNA. Error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01 by two-tailed Student’s t test. One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey-Kramer test was used.