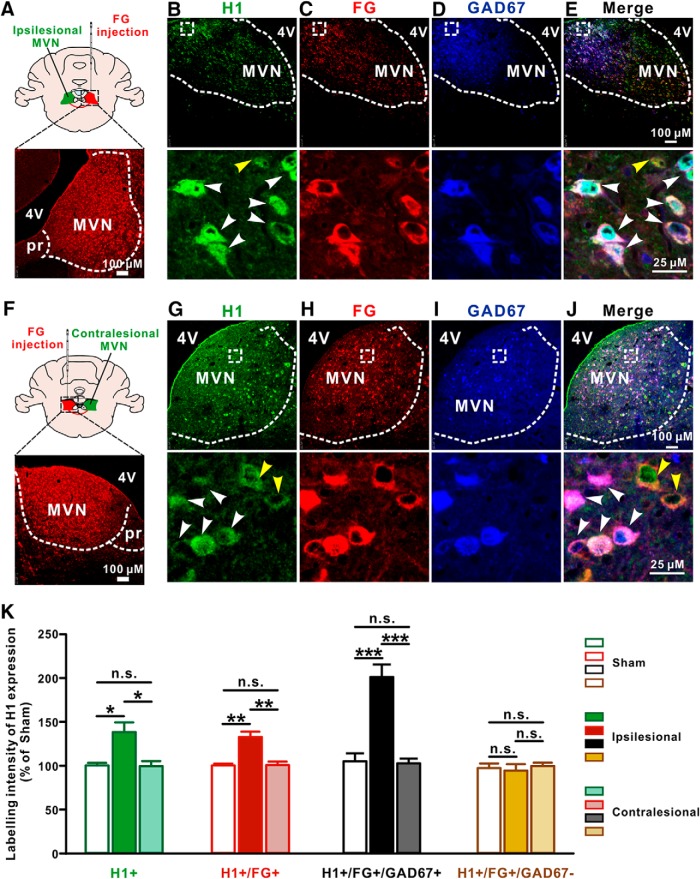
Figure 2.
The expression of H1 receptor is selectively increased in the ipsilesional GABAergic MVN commissural neurons after UL. A, Diagram and a coronal brain section showing the injection site of FG in the contralesional MVN. B–E, Triple immunostainings for H1 receptor (green; B), FG (red; C) and GAD67 (blue; D) in the ipsilesional MVN. White arrowheads in the merged image (B, E) indicate the H1/FG/GAD67 triple-labeled GABAergic MVN commissural neurons, whereas yellow arrowhead in the merged image (B, E) indicates H1/FG double-labeled non-GABAergic (glutamatergic) commissural neuron. F, Diagram and a coronal brain section showing the injection site of FG in the ipsilesional MVN. G–J, Triple immunostainings for H1 receptor (G, green), FG (H, red) and GAD67 (I, blue) in the contralesional MVN. White arrowheads in the merged image (G, J) indicate the H1/FG/GAD67 triple-labeled GABAergic MVN commissural neurons, whereas yellow arrowheads in the merged image (G, J) indicate H1/FG double-labeled non-GABAergic (glutamatergic) commissural neurons. K, Labeling intensity of H1 receptor expression in the H1+, FG+, FG+/GAD67+, and FG+/GAD67− neurons in the MVN in sham rats and the ipsilesional and contralesional MVNs in UL rats. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.01, n.s. no significant difference, by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's test. See also Figure 2-1.