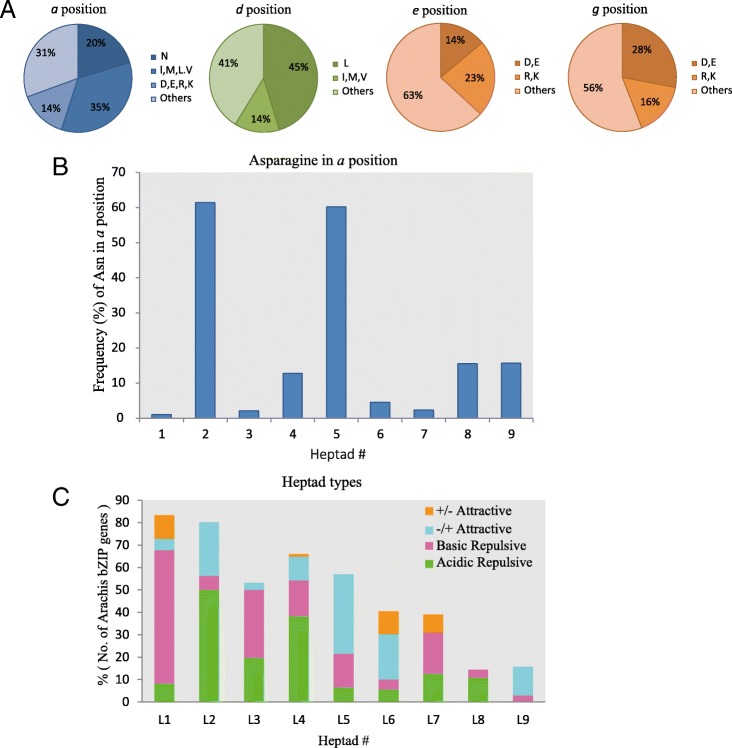
Fig. 4.
Prediction of dimerization properties of the Arachis bZIP proteins. a Pie charts indicating the frequency of various amino acids in each of the four positions (a, d, e, and g) in the Leu zipper of the Arachis bZIP domains. b Histogram of the frequency of Asn (N) in the a position of the Leu zipper across all Arachis bZIP proteins. c Histogram showing the frequency of attractive or repulsive g↔e’ pairs per heptad across all Arachis bZIP proteins. The g↔e′ pairs are classified into four groups according to the electrostatic charges at the g and e positions. The +/− attractive, showed by orange box, indicates that the g position is basic and the following e position is acidic. The −/+ attractive, showed by skyblue box, indicates that the g position is acidic and the following e position is basic. The basic repulsive (pink box) and acidic repulsive (green box) indicate that the g and the following e positions have a similar charge, either both basic or both acidic