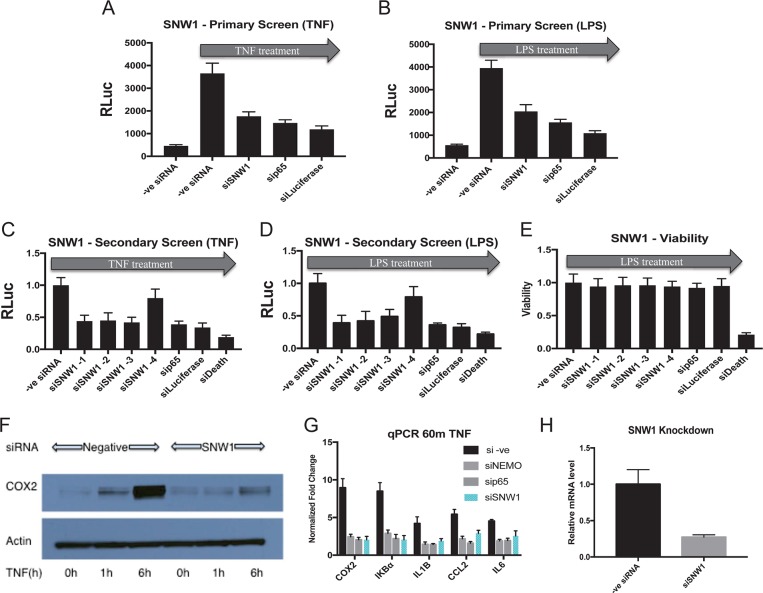
FIG 3.
SNW1 depletion attenuates NF-κB pathway activation in multiple cell lines, with minimal loss of cell viability. (A and B) Reduction of activated NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity (via TNF-α or LPS) under SNW1 RNAi (pool of 4 siRNAs) conditions in THP-1 cells (P < 0.05). The reduction is comparable to those with positive controls (RNAi against p65 or luciferase) (n = 2 replicates). RLuc, Renilla luciferase. (C and D) Three out of four individual siRNAs against SNW1 used in our secondary screen attenuated the NF-κB-dependent luciferase response upon stimulation with TNF-α or LPS (P < 0.05) (n = 3 replicates). (E) The reduction in NF-κB-dependent luciferase activity by siRNAs against SNW1 is not due to a loss of cell viability. siRNA against an essential ribosomal protein (siDeath) was used as a positive control (n = 3 replicates). (F) TNF-α-stimulated NF-κB-dependent expression of COX2 protein is attenuated in U87 cells transfected with siRNA against SNW1 (n = 2 replicates [1 replicate is shown]). (G) Knockdown of SNW1 downregulates the expression of NF-κB target genes upon TNF-α treatment in THP-1 cells, as determined by qPCR (P < 0.05 for negative-control [–ve] siRNA versus other conditions for all genes). The degree of downregulation is similar to those under sip65 and siNEMO conditions (positive controls) (n = 3 replicates). Note that the y axis shows fold changes of NF-κB target gene expression with respect to the non-TNF-α-stimulated control. (H) siSNW1 transfection leads to a reduction of SNW1 mRNA levels (P < 0.05) (n = 3 replicates).