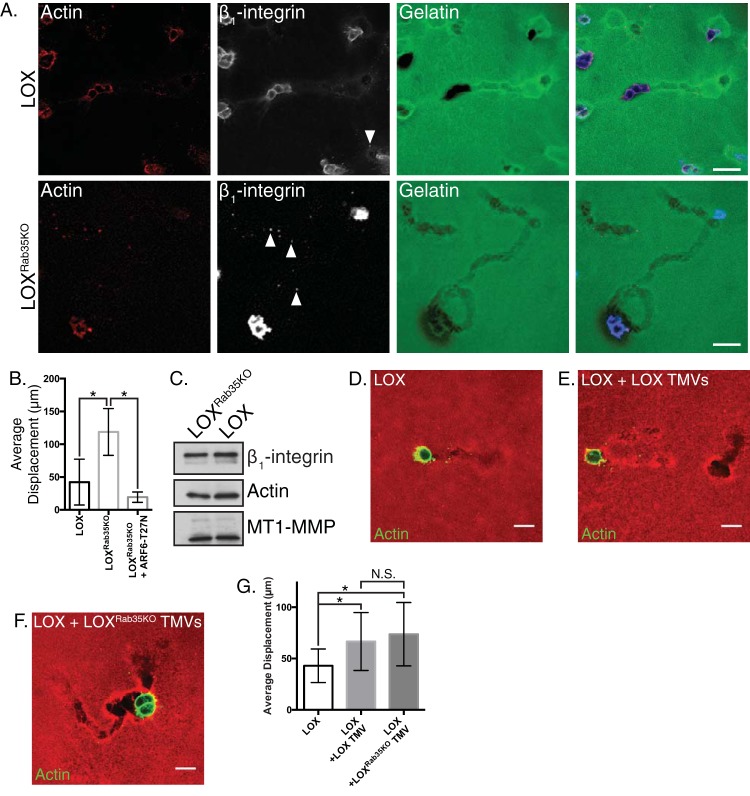
FIG 2.
Rab35 knockout facilitates amoeboid cell invasion. (A) LOX or LOXRab35KO cells were plated in an in vitro amoeboid cell invasion assay and allowed to invade for 24 h. Invasive cells were fixed, stained as indicated, and examined by confocal microscopy in order to quantify changes in invasive potential. Scale bars, 25 µm. (B) The average displacement of LOX, LOXRab35KO, and LOXRab35KO cells expressing ARF6-T27N was calculated after 8 h of invasion into compliant matrix. Data are presented as means ± the standard deviations (SD; *, P < 0.05). (C) Equal amounts of protein contained in lysates generated from TMVs isolated from LOX or LOXRab35KO cells were separated by SDS-PAGE, and the cargo content was examined as indicated by Western blotting. (D to F) Parental LOX cells alone (D) or pretreated with TMVs isolated from LOX cells (E) or LOXRab35KO cells (F) were plated in an amoeboid invasion assay. After 8 h of invasion, the cells were fixed, and the actin cytoskeleton was stained and imaged. Scale bars, 20 µm. (G) The average displacement per field of cells described for panels D to F was calculated after 8 h of invasion into compliant matrix. Data are presented as means ± the SD (*, P < 0.05; N.S., not statistically significant).