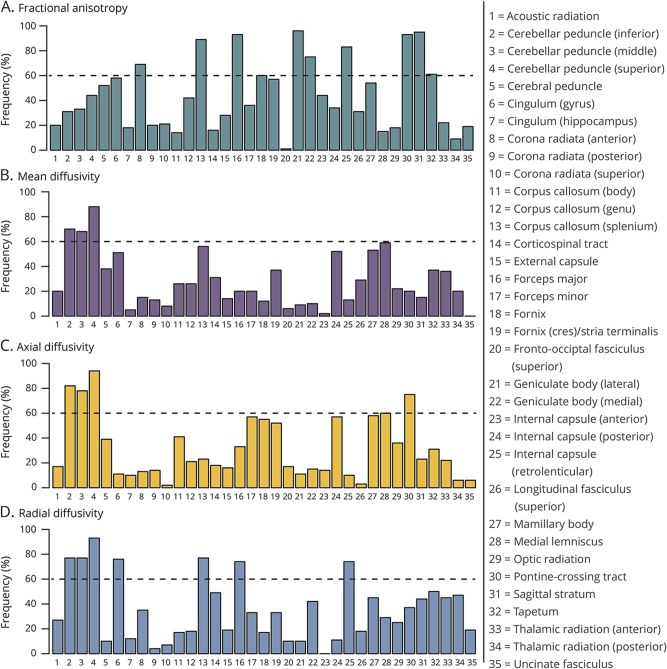
Figure 1. Bootstrap analysis.
Bootstrapping technique was applied with the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator, and each white matter tract was ranked according to the frequency at which it was chosen as important for distinguishing patients with essential tremor and Parkinson disease for each of fractional anisotropy (A), mean diffusivity (B), axial diffusivity (C), and radial diffusivity (D). Threshold of 60% was utilized to determine the most important tracts for further analysis with a region of interest approach.