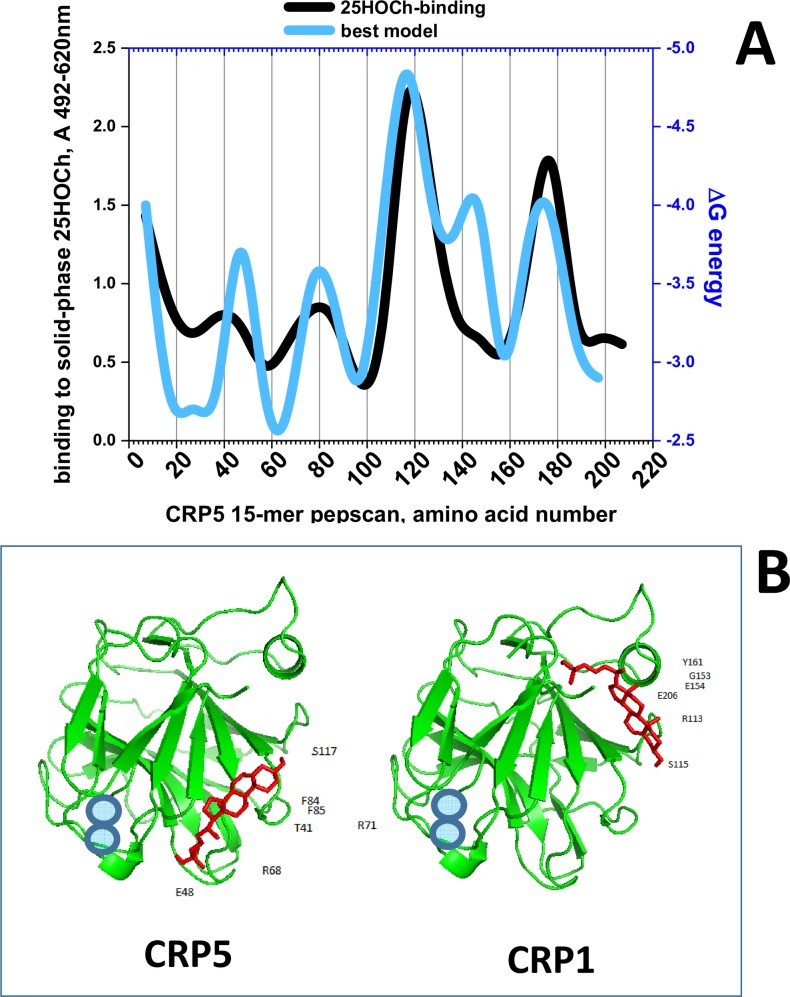
Fig 4.
Solid-phase binding and docking predictions to 25HOCh of CRP5 pepscan peptides (A) and predicted best docking location (B). A) For the peptide-binding assays, a series of 15-mer peptides overlapping 5 amino acids from CRP5 was chemically synthesized by adding an amino-terminal biotin molecule. Solid-phases were coated with 2 μg per well of 25HOCh into polystyrene 96-well plates. The binding of 0.05 μg of biotinylated pepscan peptides, detection with peroxidase-labeled streptavidin and staining with OPD were then performed. The means from 3 independent experiments were represented and standard deviations omitted for clarity (S5 Table). For the in silico docking predictions, the modeled pepscan peptides with the lowest energies were docked to several possible conformations of 25HOCh as described in the methods section. The docking energies that best fitted the binding data were then represented (S5 Table). Black line, peptide binding to 25HOCh. Blue line, predicted ΔG energy of peptide docking to 25HOCh. B) PyMOL representation of the lowest energy structures of CRP5 and CRP1 complexed to 25HOCh (the remaining CRP1-7 were similar). Green, CRP amino acid chains. Red, 25HOCh. Blue circles, Ca++ atoms located at the PC-binding pocket [6].