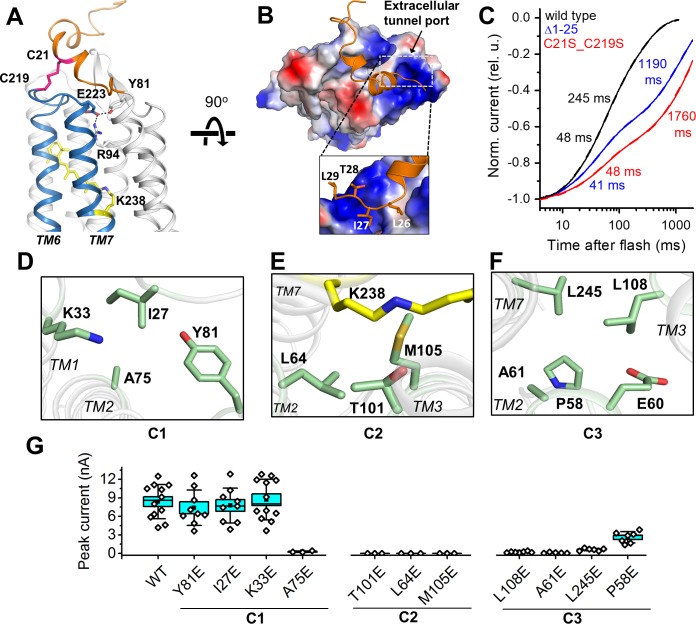
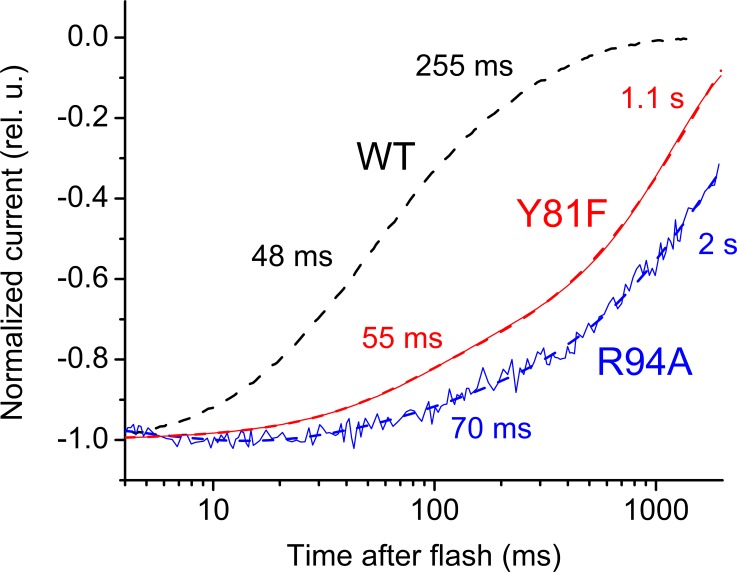
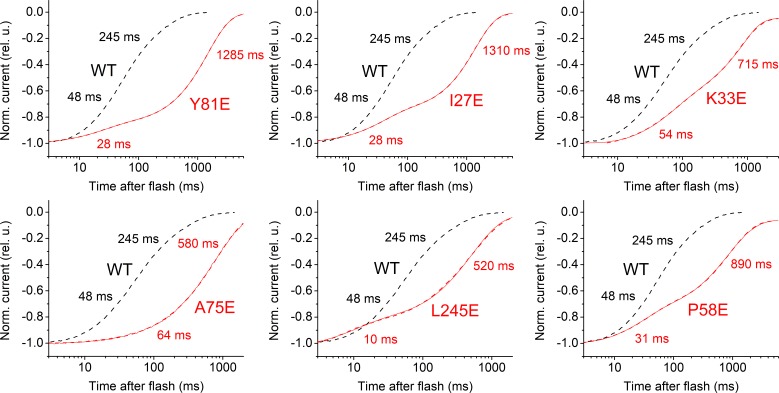
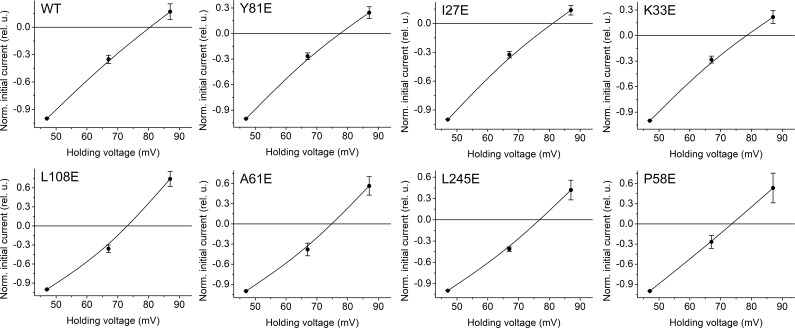
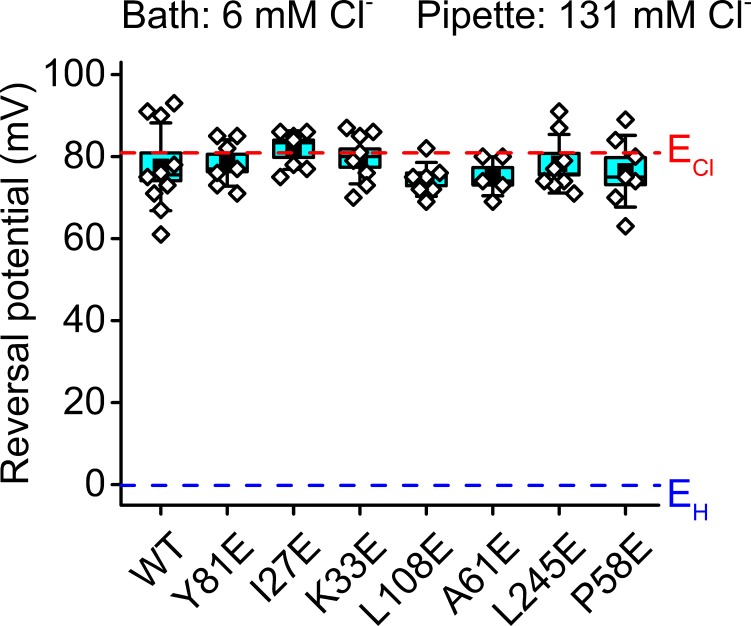
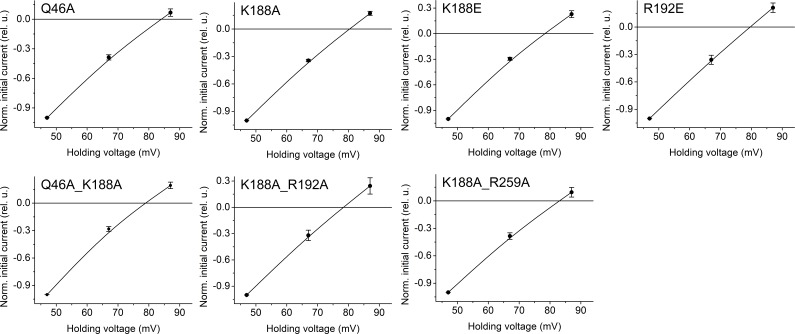
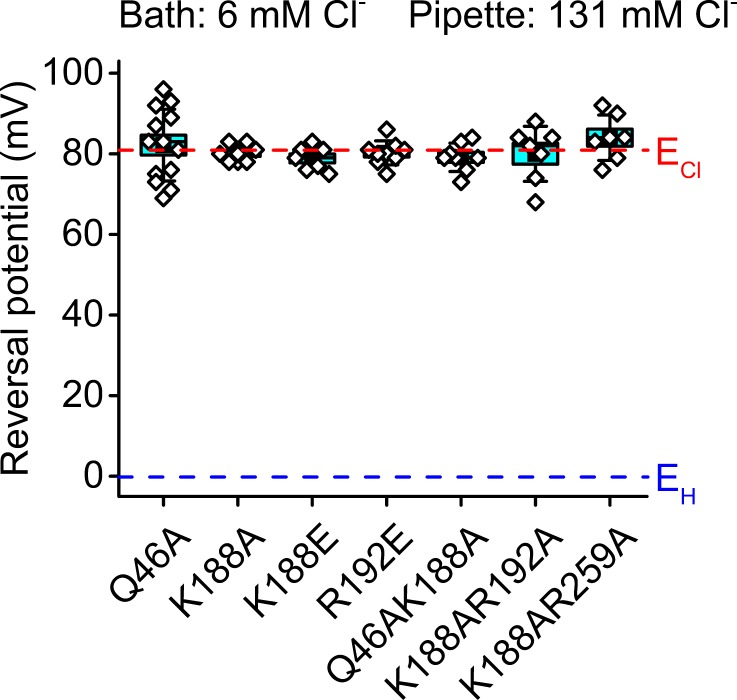
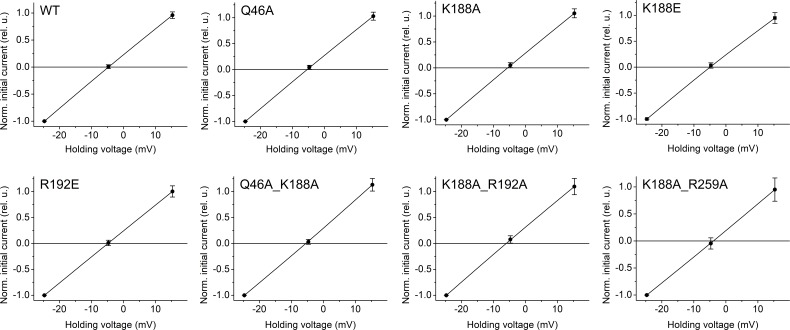
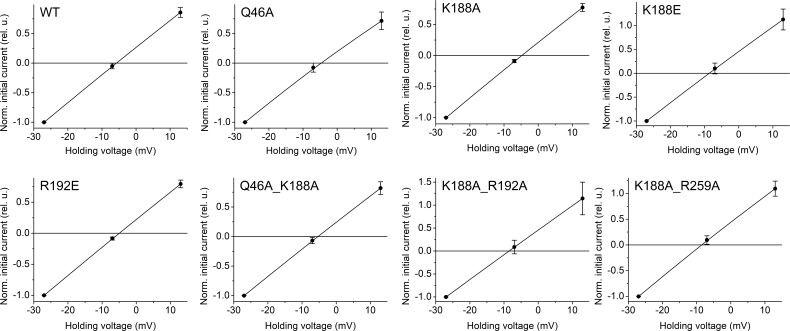
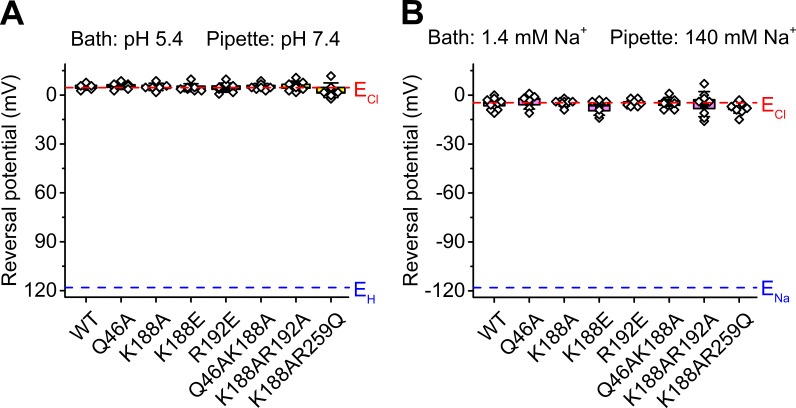
Figure 3. Features of the ion pathway of GtACR1.
(A) The N-terminal extracellular loop (orange) immobilized by an intracellular C21-C219 disulfide bridge (red) to the TM6-7 loop (blue); an H-bond network (black dashed lines) formed by residues (sticks) near the extracellular port. (B) The hydrophobic segment (orange) blocks the extracellular port rendered by the electrostatic potential surface. Rectangle: closer (rotated) view of the peptide cap conformation. (C) Decay kinetics of laser flash-evoked photocurrents by the wild-type GtACR1 and indicated mutants. (D–F) The structure of the three constrictions: C1 (D), C2 (E), and C3 (F). (G) Peak photocurrents generated by Glu substitutions of the constriction residues in response to a 1 s light pulse (515 nm, 7.7 mW mm−2) with 131 mM Cl- in the pipette and 6 mM Cl- in the bath. The black squares, mean; line, median; box, SE; whiskers, SD; empty diamonds, raw data recorded from individual cells.