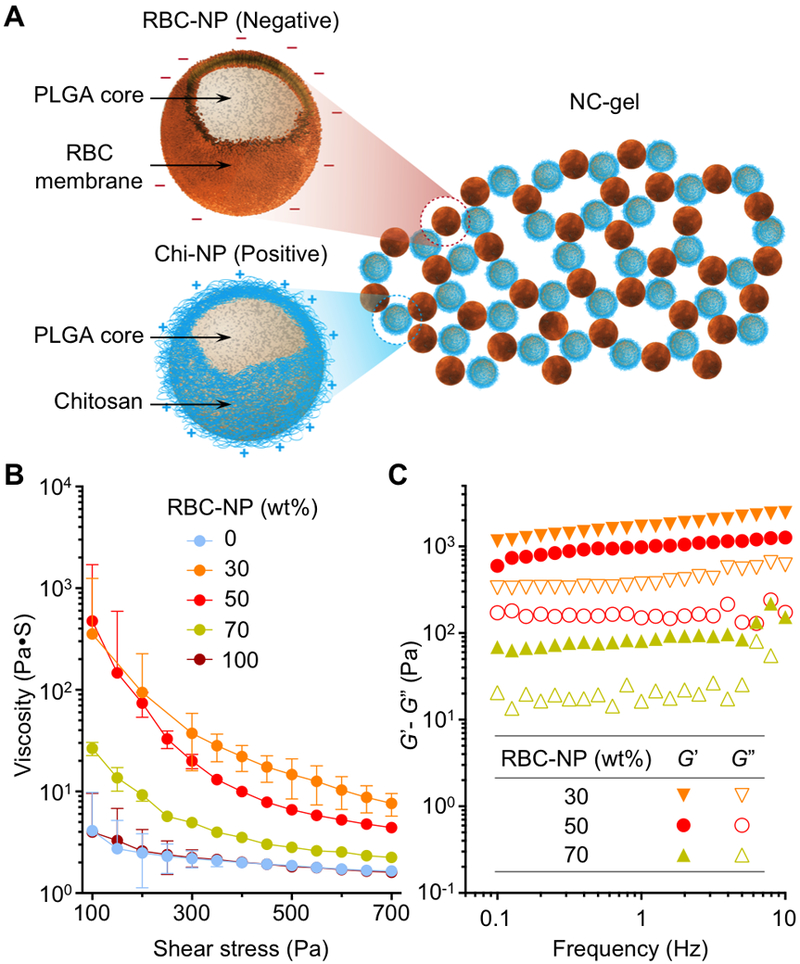
Figure 1. Preparation of nanosponge colloidal gel (denoted ‘NC-gel’).
(A) Schematic illustration of NC-gel formulation by mixing red blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles (RBC-NPs), which possess a negative surface charge, with chitosan-modified nanoparticles (Chi-NPs) as positively charged nanoparticle counterparts. (B) RBC-NPs and Chi-NPs mixed at different mass ratios (0, 30, 50, 70, and 100 wt% of RBC-NP, respectively) were measured for viscosity with varying shear stress (100–700 Pa). (C) RBC-NPs and Chi-NPs mixed at different mass ratios (30, 50, and 70 wt% of RBC-NP, respectively) were measured for the storage modulus G’ and loss modulus G’’ against frequency (0.1–10 Hz). All rheological measurements were performed at 25°C.