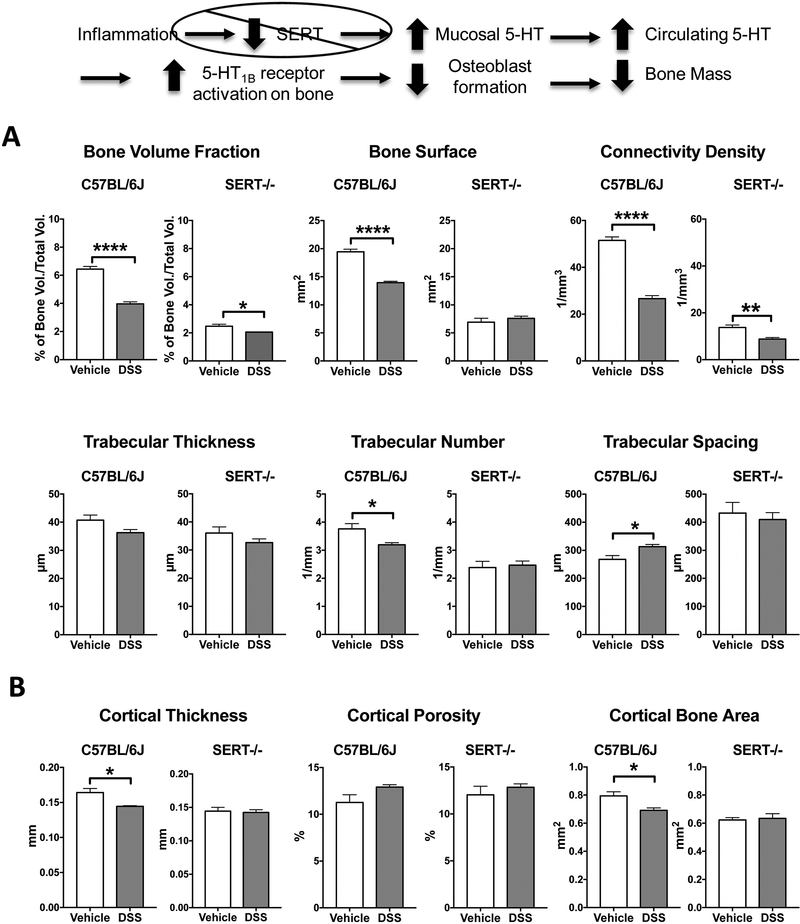
Figure 1:
Effects of DSS colitis on features of trabecular (A) and cortical (B) bone in C57BL6/J and SERT-/- mice. Morphometric analysis of the femurs of DSS-inflamed C57BL6/J mice showed deficits in trabecular bone. Only trabecular thickness remained unchanged after chronic DSS treatment when compared to control. SERT-/- mice drinking water had lower bone volume fraction, bone surface and connective density as well as reduced trabecular number and increased trabecular spacing when compared to control C57BL6/J mice. Of these trabecular bone measurements, only bone volume fraction and connective density were further decreased following DSS-induced inflammation. Of the cortical bone measurements, only cortical thickness was affected by colitis. C57BL6/J+Vehicle, n=5; C57BL6/J+DSS, n=5; SERT-/- +Vehicle, n= 4; SERT-/- + DSS, n=4. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001; unpaired 2-tailed student’s t-test.