Figure 4.
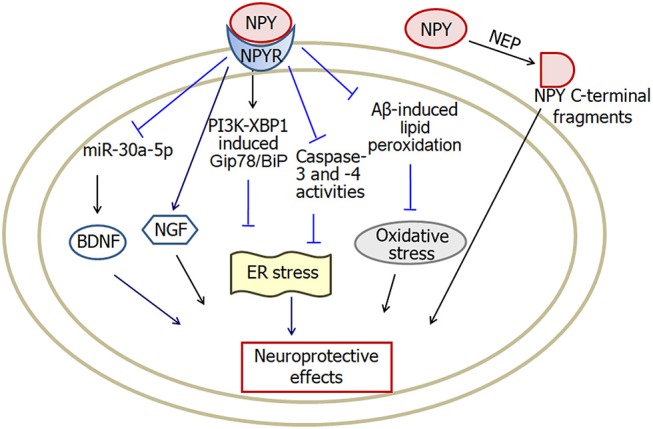
A model showing the possible pathways of neuropeptide Y-induced neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropeptide Y inhibits Aβ-induced lipid peroxidation and prevents intracellular oxidative stress. Activation of PI3K-XBP1 pathway may also be involved in neuropeptide Y-induced neuroprotection against endoplasmic reticulum stress. Moreover, both NGF and BDNF are involved in neuropeptide Y-induced neuroprotective effects. In addition, NEP cleaves neuropeptide Y into C-terminal fragments, which protect against the neurodegenerative pathology in Alzheimer's disease. NPY, neuropeptide Y; NPYR, neuropeptide Y receptors; NEP, neutral endopeptidase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NGF, nerve growth factor. The internal and external circles represent the inner and outer leaflets of the cellular membrane.
