Fig. 8. Establishment of two T-cell cultures specific for mutant CALR epitopes.
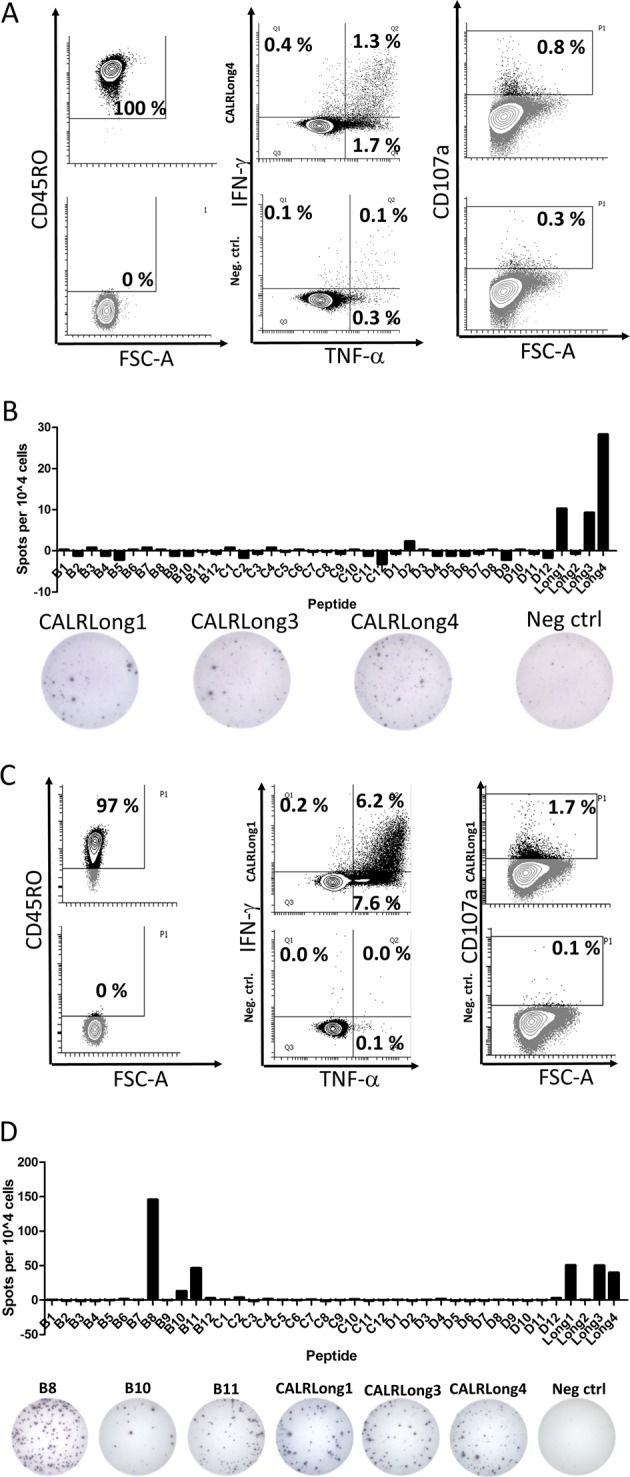
a (Left) Purity analysis of isolated CD4+ T-memory cells with cells stained for CD45RO (top, left) and cells that were unstained (below, left). The percentages depict the amount of CD45RO+ cells from the CD3+ fraction. After three stimulations with autologous DC cells were analyzed for cytokine release against CALRLong4 (top, middle) and scrambled negative control peptide (below, middle). Cells were also analyzed for expression of CD107a upon stimulation with CALRLong4 (top, right) and negative control peptide (below, right). b The T-cell culture was analyzed for responses against the CALR library and several other CALR-mutant epitopes with the amount of spots shown (top), and representative wells displayed (below). c CD4+ T-memory cells were isolated from another donor and used to establish a T-cell culture specific for the CALRLong1 epitope. Purity analysis (left), cytokine release (middle), and CD107a upregulation were analyzed as in a. d The CALRLong1 specific T-cell culture was analyzed for responses against the CALR library. We identified responses against several short epitopes from the CALR library as well as long epitopes (top). Representative wells are shown (below)
