Figure 5.
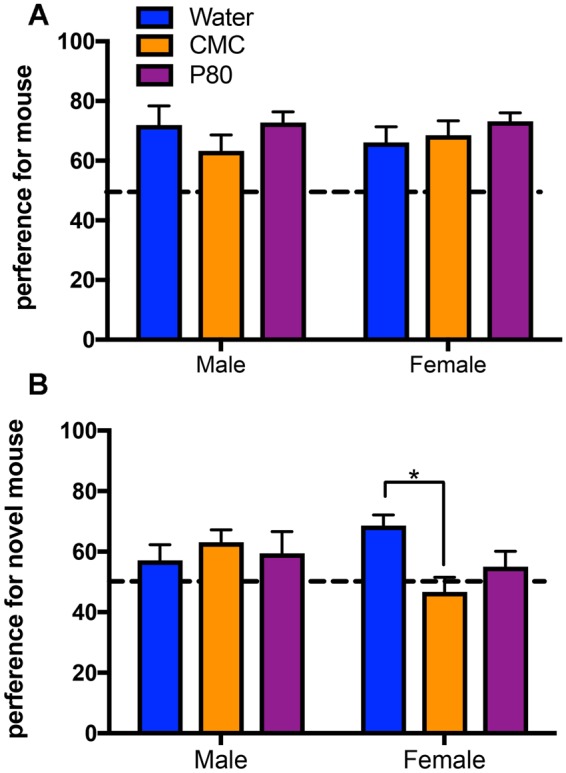
Dietary emulsifiers decrease preference for social novelty in female mice. (A) There was no significant main effect of emulsifier consumption [F(2,28) = 1.08, p = 0.35] or sex [F(1,28) = 0.00003 p = 0.99] on the preference for investigating a novel, conspecific mouse during the sociability test in the three-chambered sociability apparatus. In addition, there was no sex by treatment interaction on this measure [F(2,28) = 0.67, p = 0.52] (B). Emulsifier treatment and sex interacted on the preference for investigating a second novel, conspecific mouse during the preference for social novelty test in the three-chambered sociability apparatus [F(2,29) = 3.71, p < 0.05]. In addition, post-hoc comparisons indicate that treatment with CMC significantly decreased the preferences of female mice for the novel mouse (*p < 0.05). Data are represented as means + SEM (n = 5–6).
