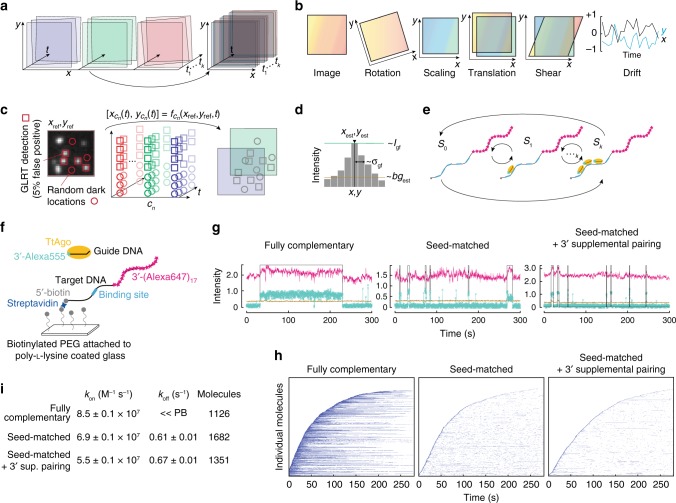
Fig. 1.
Automated Bayesian single-molecule pipeline for binding assays. a Multiple color channels are registered and corrected for drift. b Estimated mapping between the colors is time-dependent and consists of rotation, scaling, translation, and drift. c Generalized likelihood ratio test (GRLT) is used to detect initial positions of target molecules (xref, yref) in one channel. These locations are then mapped to other channels cn (n being number of the channel), and are extracted to estimate signal and background parameters. d Estimated parameters include the position (xest, yest), background bgest, intensity Igf and width σgf of the single-molecule. e Variational Bayesian Evidence Maximization of Multivariate Gaussian Hidden Markov Model (VBEM-MGHMM) is used to cluster the complexity and estimate parameters of the underlying kinetics. S0, S1 and Sk are bound states 0, 1 and k, respectively. f Experimental set-up to measure TtAgo:guide interactions with target DNA. g Representative fluorescence intensity time traces of TtAgo (turquoise) binding DNA target (magenta) with different extents of complementarity to the DNA guide. Light brown indicates background levels of green fluorescence, whereas the black line denotes binding events detected by the pipeline after event filtering (minimal duration and gap closing; see User Manual—Co-localization analysis). Fluorescence intensity is expressed in thousands of photons. Increase in red fluorescence correlated with the arrival of TtAgo:guide complex (green) is Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) from the Alexa555 guide to the Alexa647 target. h Rastergram summary of traces of individual target molecules, each in a single row and sorted according to their arrival time, for different guide:target pairings. i Comparison of kon and koff of TtAgo with different targets. Values were derived from data collected from several hundred individual DNA target molecules (indicated as number of molecules); standard error from bootstrapping is reported. « PB: not determined because koff was slower than the rate of photobleaching