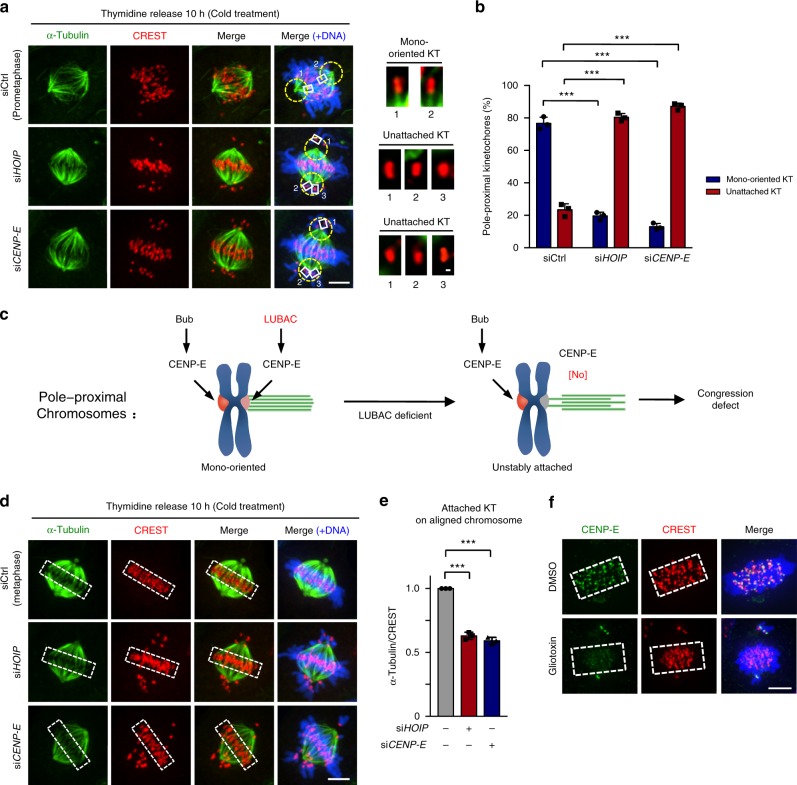
Fig. 3.
LUBAC regulates KT-MT attachment, chromosome congression and alignment. a Cold-stable microtubules at pole-proximal kinetochores in control, HOIP or CENP-E depleted mitotic cells. Green, α-Tubulin; red, CREST; blue, DNA. Yellow circles indicate the pole-proximal region (an area covered by a circle with 2.5 μm in radius centered around the spindle pole). Insets show mono-oriented or unattached pole-proximal kinetochores in each group. b Percentage of mono-oriented or unattached pole-proximal kinetochores in control (n = 29 cells), HOIP (n = 25 cells) or CENP-E (n = 25 cells) depleted cells. c Model of LUBAC-dependent CENP-E localization at attached kinetochores on pole-proximal chromosomes regulating KT-MT attachment and chromosome congression. d Cold-stable microtubules on aligned chromosomes in control, HOIP or CENP-E depleted mitotic cells. Green, α-Tubulin; red, CREST; blue, DNA. White dashed boxes indicate areas where α-tubulin intensity was measured. e Relative intensity of cold-stable k-fibers of the attached kinetochores on aligned chromosomes in control, HOIP or CENP-E depleted cells in d. n = 15 cells per group. The average α-tubulin/CREST ratio of each group was normalized to control cells. f CENP-E kinetochore localization in HeLa cells treated with 100 nM proteasome inhibitor Velcade for 2 h, and then released into medium containing DMSO or 1.2 μM Gliotoxin (LUBAC inhibitor) for 30 min. Green, CENP-E; red, CREST; blue, DNA. Dashed boxes, regions of aligned chromosomes. Data are presented as mean ± s.d. of three independent experiments (b and e). Dashed boxes, regions of aligned chromosomes (d and f). ***P < 0.001; two-sided Student’s t-test. Scale bars, 5 μm (main image) and 0.3 μm (magnified region)