FIGURE 2.
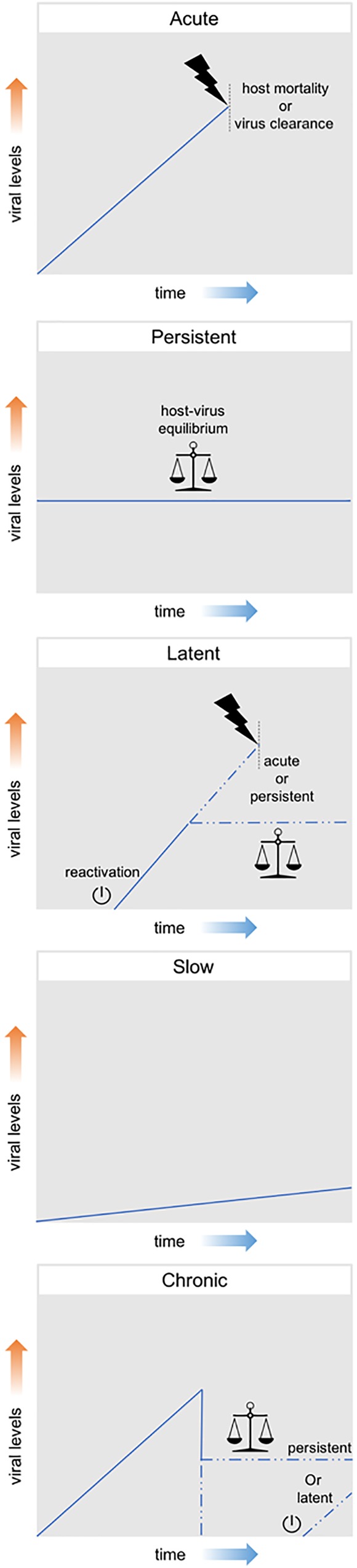
Patterns of viral infection. Acute infections are represented by a high increase in viral levels and are limited in time either by the death of the host or by the clearance of the virus by the host immune system. Persistent infections consist in constant, but relatively low, viral levels and can manifest themselves for long periods of time. Latent infections consist in the presence of the viral genome in the host cell without actual production of viral particles. During this latency, viruses maintain the potential to resume viral replication and start producing viral particles (reactivation). Chronic infections are generally defined as the outcome of an acute infection in which neither host mortality nor virus clearance occur, meaning a persistent or latent outcome derived from an acute infection. Slow infections are characterized by a slow, but not constant, increasing in viral levels overtime.
