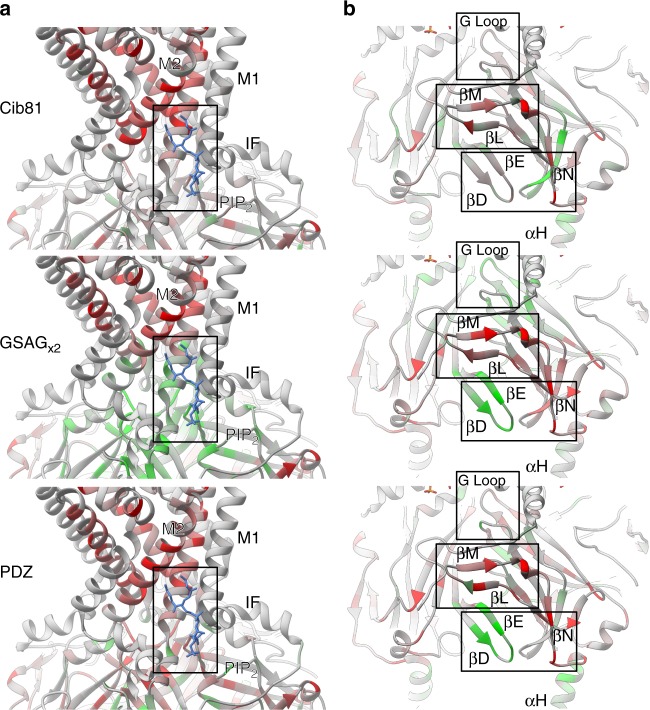
Fig. 3.
Differential domain insertion permissibility. Permissibility data is mapped on the crystal structure of chicken Kir2.2 (PDB 3SPI). Domain insertion permissibility for three different domains (indicated on the left) is shown colored increasing from red to green. a All types of insertions into transmembrane helixes (e.g., M2) are strongly selected against. Permissibility in PIP2 binding site (boxed) depends on structural context of the insertion. b Some non-conserved, surface-exposed loops (e.g., βN) were not permissive, while the βD–βE loop (which binds Gβγ in GIRK) and the G-loop (βH–βI, the cytoplasmic gate in Kir2.1) have context-dependent permissibility (i.e., permissive for GSAGx2 and PDZ insertion, less permissive for Cib81 insertion)