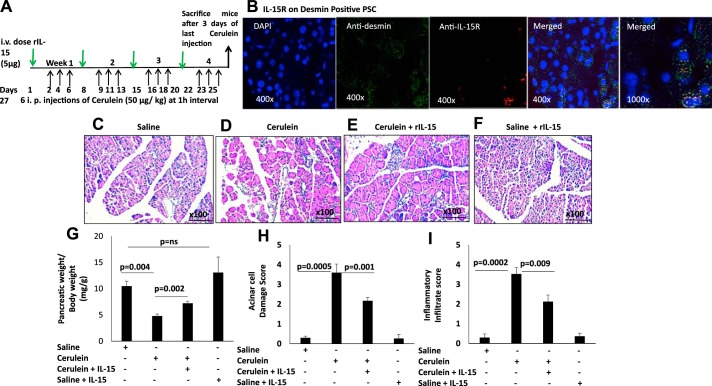
Fig. 2.
Interleukin (IL)-15 pretreatment ameliorates the pathogenesis of cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis. A: experimental protocol of cerulein-induced chronic pancreatitis in a mouse model. Green arrows, dose of recombinant (r) IL-15; black arrows, ip cerulein injection during the experimental protocol. B: a representative immunofluorescence analysis detected IL-15 receptor (IL-15R) on anti-desmin-positive pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs); original magnification ×400 and ×1,000. C–F: photomicrograph of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained representative pancreatic tissue section of saline-treated (C), cerulein-treated (D), cerulein with rIL-15-treated (E), and saline + rIL-15 treated (F) mice. G–I: ratio of pancreas/mouse body weight (G), acinar cell damage (H), and inflammatory cell (I) analysis on a 0–4 scale in saline-, cerulein-, cerulein with IL-15-, and saline + IL-15-treated mice. Data are presented as means ± SD; n = 6–8 mice/group. All photomicrographs shown have the original magnification of ×100.