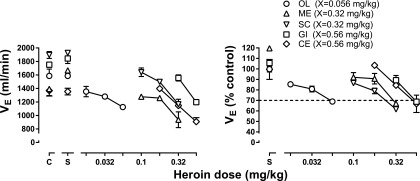
Fig. 1.
Potency for heroin to decrease respiration across monkeys. The average of two heroin dose-effect curves determined in the absence of antagonist are shown with each symbol representing data from a different monkey. Because the potency of heroin varied across monkeys, the smallest dose of heroin that decreased VE to <70% of control was designated dose X and used to normalize dose-effect curves to compare results of antagonism studies (Figs. 2 and 4). Abscissae: heroin dose in milligrams per kilogram of body weight. Ordinates: minute volume (VE) in milliliters per minute (left) or expressed as a percentage of control, which was obtained from the last 5 minutes of the control period for that session (right).