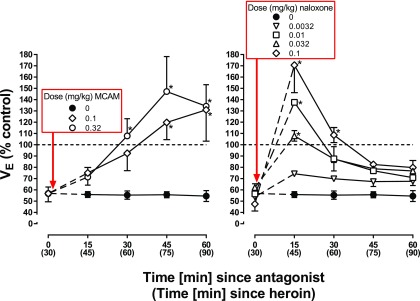
Fig. 3.
Reversal of the respiratory-depressant effects of heroin in four monkeys. A dose of heroin that decreased VE to <70% of control when given as a bolus injection was administered with a second injection of either saline, MCAM, or naloxone given 30 minutes later. The dose of heroin needed to produce this effect varied across monkeys (OL: 0.1 mg/kg, ME: 0.32 mg/kg, SC: 0.56 mg/kg, and GI: 1 mg/kg). Asterisks indicate that data points obtained following administration of an antagonist are significantly greater than those obtained with heroin alone. Abscissae: time since administration of the second injection with time since heroin administration shown in parentheses. Ordinates: minute volume (VE) expressed as a percentage of control.