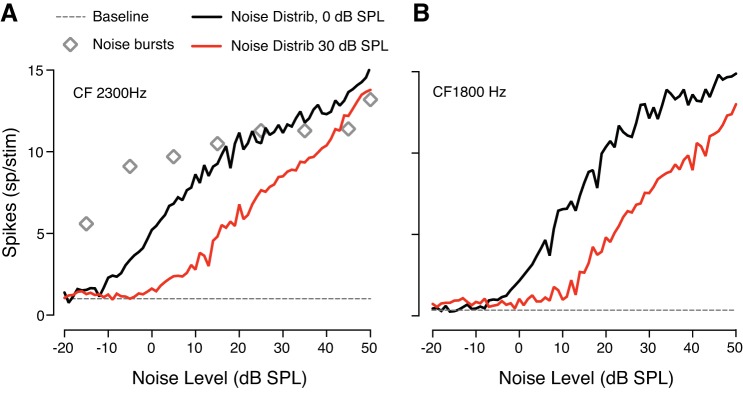
Fig. 2.
Responses of inferior colliculus (IC) units to two distributions of noise amplitudes [0 and 30 dB sound pressure level (SPL)]. Monkeys passively listed to band-limited white noise presented in absence of tone. Rate versus level functions adapt to the mean sound level also in awake, behaving subjects. A: firing rate for a neuron tuned to 2300 Hz. The black line shows neuronal response to a distribution of noise amplitudes centered on 0 dB SPL spectrum level. The red line represents the adapted response of the same neuron to a noise distribution with a mean level of 30 dB SPL spectrum level. Open symbols indicate the response of the same neuron to bursts of noise. The dashed line shows the baseline activity when no noise was played. B: response of an IC neuron with a characteristic frequency (CF) of 1800 Hz.