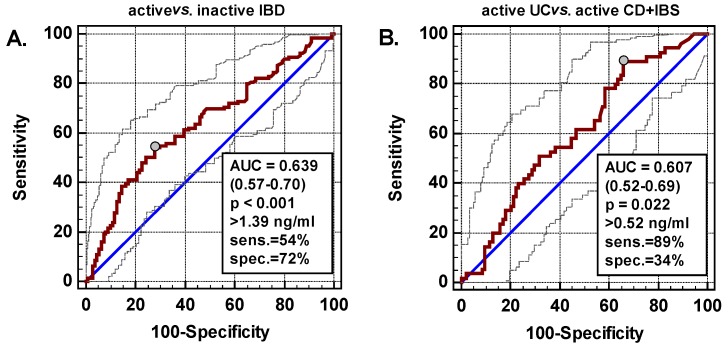
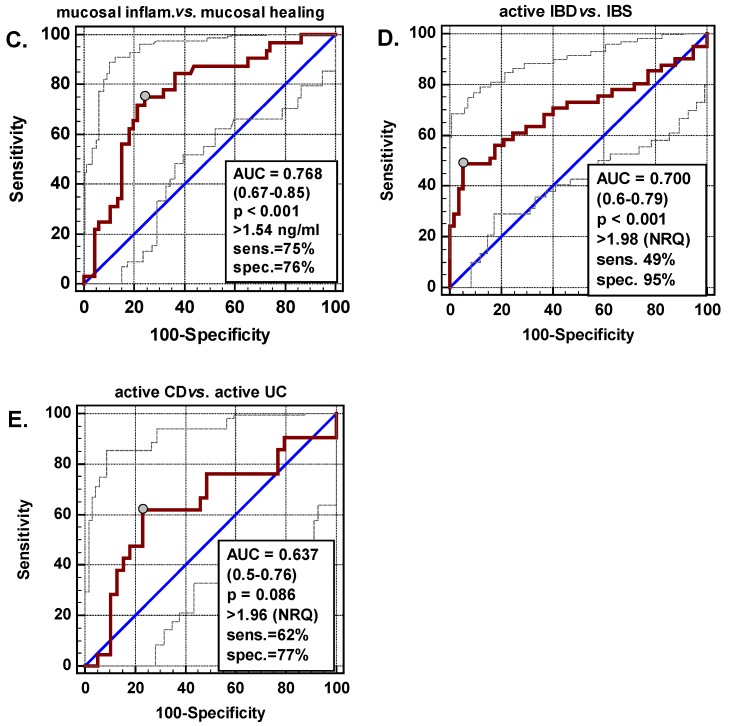
Figure 2.
Nampt as an IBD marker. (A) S-Nampt as a marker differentiating patients with active and non-active disease; (B) S-Nampt as a marker differentiating patients with active UC from those with active CD and IBS; (C) S-Nampt as a marker differentiating UC patients with mucosal inflammation (Mayo endoscopic scores 2 and 3) from those without (scores 0 and 1); (D) L-Nampt as a marker differentiating IBD patients with active disease from IBS; (E) L-Nampt as a marker differentiating patients with active CD from active UC. Data are presented as ROC curves (straight line) with 95% confidence interval (CI) (dashed lines). Diagonal line presents the performance of a chance marker for which AUC = 0.5. Grey circle indicates optimal cut-off. Boxes contain data on the AUCs with 95%CI and probabilities of them being significantly different from a chance marker, optimal cut-offs with corresponding sensitivities and specificities. IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; CD, Crohn’s disease; UC, ulcerative colitis; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; inflam., inflammation; AUC, area under receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve; sens., sensitivity; spec., specificity.