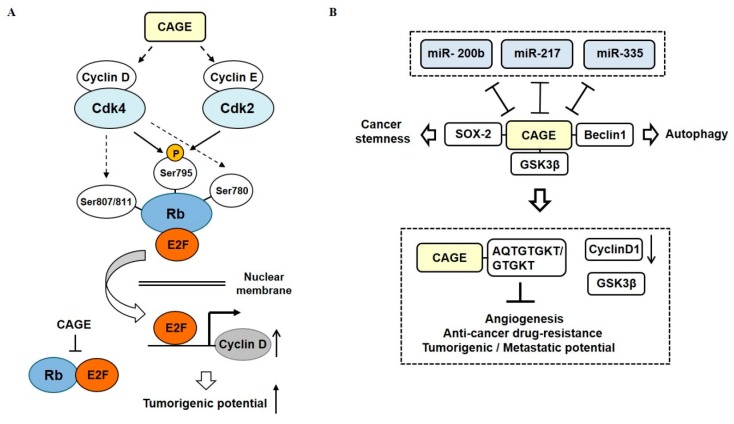
Figure 6.
CAGE-miRNA network in anti-cancer drug resistance. (A) CAGE increases expression levels of cyclins, which in turn increases cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activities. Increased CDK activities phosphorylate Rb to inactivate the Rb protein. Inactivation of Rb leads to the activation of E2 factor (E2F). Activated E2F binds to promoter sequences of cyclins. (B) MiR-200b, miR-217, and miR-335 form negative feedback loops with CAGE. CAGE binds to GSK3β, which increases expression of cyclin D1 to confer resistance to anti-cancer drugs. AQTGTGKT, as a CAGE-derived peptide can disrupt the interaction between CAGE and GSK3β and confer sensitivity to anti-cancer drugs. The T-bar arrows denote negative regulation and both side T-bar arrows denote cross inhibition. The hollow arrows denote positive regulation.