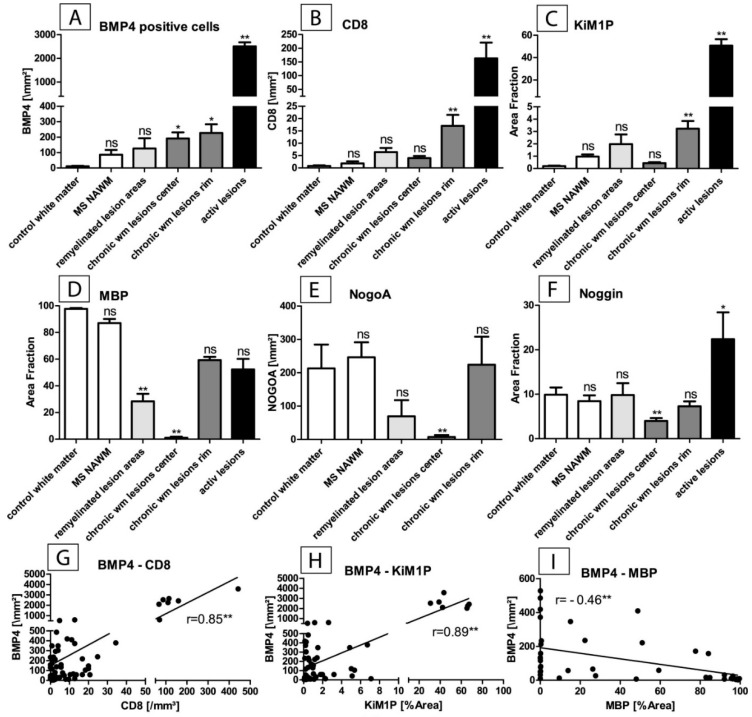
Figure 3.
Software-assisted immunohistochemical quantification of BMP4-positive cells associated with the white matter pathology of multiple sclerosis: (A) Quantification of immunopositive cells in inflammatory i.e., active lesions, the lesion margin of chronically inactive lesions, the lesion center of chronically inactive lesions, remyelinated lesion sites and normal appearing white matter (NAWM) of MS cases with respect to control tissue (white matter of cases without apparent neurological disease). A significantly increased number of BMP4-positive cells is found in active lesions. A larger number of BMP4-positive cells are also seen in the periphery and center of chronically inactive lesions (** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, n = 6–18, mean + SEM, ns = not significant). (B,C) Quantification of CD8-positive T-cells and the microglial/macrophagocytic infiltrate (CD68 (KiM1P) area fraction) in corresponding lesion areas as described under A. Inflammatory T-cellular infiltrate and microglial/macrophagocytic infiltrate are particularly present in active lesions and in the margins of chronically inactive lesions (** p < 0.01, n = 6–18, mean + SEM, ns = not significant). (D,E) Quantification of the abundance of myelin sheaths (detected by staining for the myelin protein MBP; MBP area fraction) and of mature oligodendrocytes (NogoA-staining). Compared to control tissue, myelin sheaths (D) are reduced particularly in the chronically inactive lesion centers and also in remyelinated lesion sites (** p < 0.01, n = 6–18, mean + SEM, ns = not significant). The number of mature oligodendrocytes (NogoA-staining, E) is significantly reduced only in the lesion centers of chronically inactive lesions. In the remyelinated lesion areas, their number has increased again and there is no significant difference compared to control tissue. (** p < 0.01, n = 6–18, mean + SEM, ns = not significant). (F) Quantification of the BMP4 antagonist Noggin (area fraction). Increased expression is observed in inflammatory lesions. Especially in lesion centers of chronically inactive lesions, one observes a considerably reduced expression of Noggin. There is a marked difference between the lesion centers of chronically inactive lesions and remyelinated lesion sites in which Noggin expression is restored. Both the inflammatory T-cellular infiltrate and the microglial infiltrate correlate with the number of BMP4-positive cells (** p < 0.01, r = 0.85 (G), and r = 0.89 (H)). A negative correlation between BMP4 expression and myelin sheathing is observed (** p < 0.01, r = −0.46 (I).