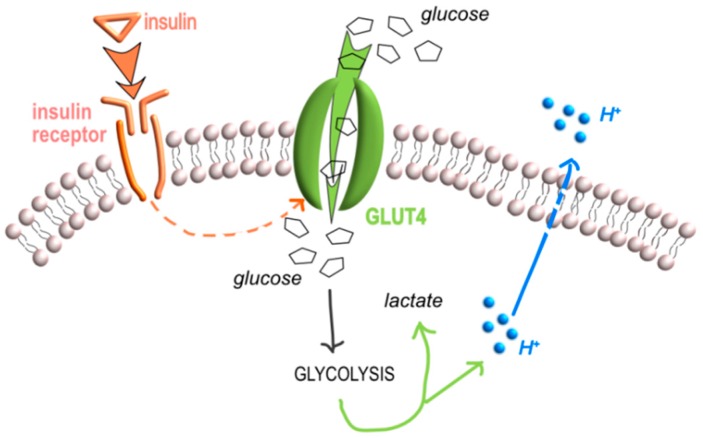
Figure 1.
Insulin stimulation produces extracellular acidification. The insulin stimulated glucose uptake from the glucose transporters (GLUT) and glycolysis. Accumulation of lactate from glycolysis leads to a progressive increment of lactate and proton concentration. Protons are then transported across the cell membrane through several transporters, including monocarboxylate transporters (MCT), that also transport lactate to the extracellular space (orange arrow, the route of insulin; green allows, the route of the products of glycolysis, lactate and protons; blue arrow, the route of protons).