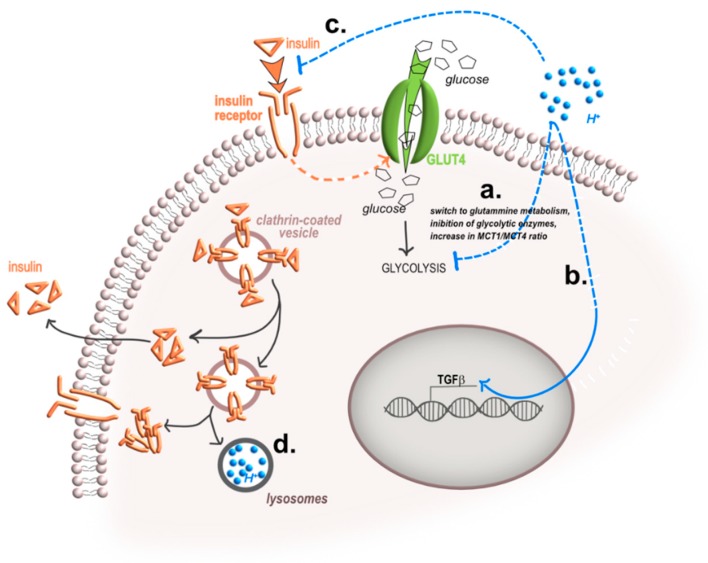
Figure 2.
Effects of acidosis on insulin sensitivity and release. Low extracellular pH may interfere with insulin sensitivity and release in different ways. (a) Acidosis switches the cellular metabolism from glycolysis to other metabolic pathways, like glutamine metabolism via the Sirtuin 1 (SIRT-1) deacetylase activity that deacetylates hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) proteins, or via the inhibition of the expression of glycolytic enzymes or through the increase of monocarboxylate transporter MCT1/MCT4 pathway; (b) acidosis induces the transcription and the protein expression of TGF-β that, in turn, inhibits insulin release at the systemic level; (c) acidosis reduces at least 40% the binding affinity between insulin and IR; (d) acidosis interferes with the recycling process of both IR and insulin, by modifying the lysosome intraluminal pH and the number of lysosomes (blue arrow, the route of protons, black arrows, the route of insulin/IR complexes; T-bar, inhibition).