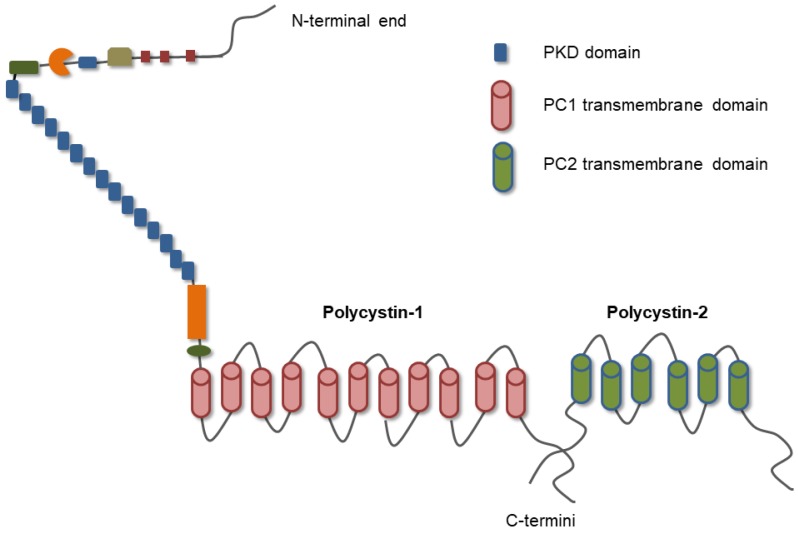
Figure 1.
Molecular structure of polycystins. Polycystin-1 has a long N-terminal end with 16 copies of the polycystic kidney disease (PKD) domain and additional domains for cell-to-cell and cell-to-matrix interactions. It has eleven transmembrane domains and a C-terminus that interacts with the Polycystin-2 C-terminus, therefore functioning as a protein complex. Polycystin-2 has six transmembrane domains and both ends are intracellular or in the interior of cell organelles, such as the endoplasmic reticulum. PC1, polycystin-1; PC2, polycystin-2 (Reprinted from Reference [8], © 2015, with permission from Elsevier).