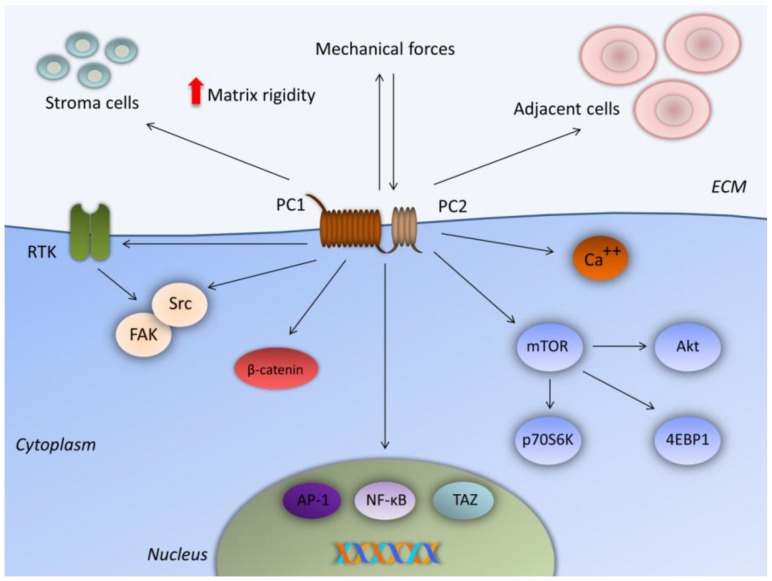
Figure 2.
Proposed mechanisms of polycystins implication in CRC. PC1 senses extracellular mechanical cues and regulates cell-to-cell and cell-to-ECM interactions in order to potentially increase matrix rigidity. PC2 mediates alterations in calcium influx and activates the mTOR signaling pathway. PC1 may also mediate cancer cell properties through β-catenin (Wnt pathway) and interacts with focal adhesion molecules (FAK, Src) and RTKs. Finally, PC1 regulates the activity of downstream transcription factors (AP-1, NF-κB, TAZ) through the PC1-CTT. CRC, colorectal cancer; 4EBP1, 4E binding protein 1; AP-1, activator protein-1; CTT, C-terminal intracellular tail; ECM, extracellular matrix; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappaB; PC1, polycystin-1; PC2, polycystin-2; p70S6K, p70S6 kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif