Figure 1.
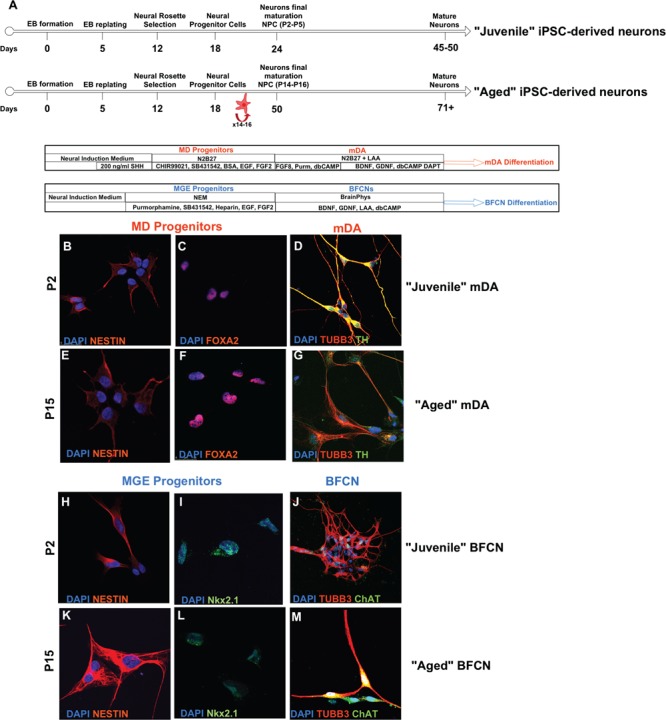
Differentiation of Juvenile and Aged hiPSC-derived neurons. (A) Timeline of the differentiation steps of Juvenile and Aged hiPSC-derived mDA and BFCN. (B–M) Representative immunocytochemistry images throughout the differentiation protocols from Control hiPSCs. (B and C) MD progenitors and (H and I) MGE progenitors co-expressed Nestin and FoxA2, and Nestin and Nkx2.1 at P2. (D) Juvenile mDA neurons and (J) Juvenile BFCN, differentiated from P2–P5 NPCs, were characterized for the co-expression of the mature neuronal marker TUBB3 and TH, and TUBB3 and ChAT, respectively. After prolonged passaging (E and F) MD progenitors and (K and L) MGE progenitors retain the co-expression of Nestin and FoxA2 and Nestin and Nkx2.1. (G) Aged mDA neurons and (M) Juvenile BFCN were successfully differentiated from P14–P16 NPCs, and they showed the co-expression of the mature neuronal marker TUBB3 and TH, and TUBB3 and ChAT, respectively. See also Supplementary Material, Figures S1–S5.
