Figure 7.
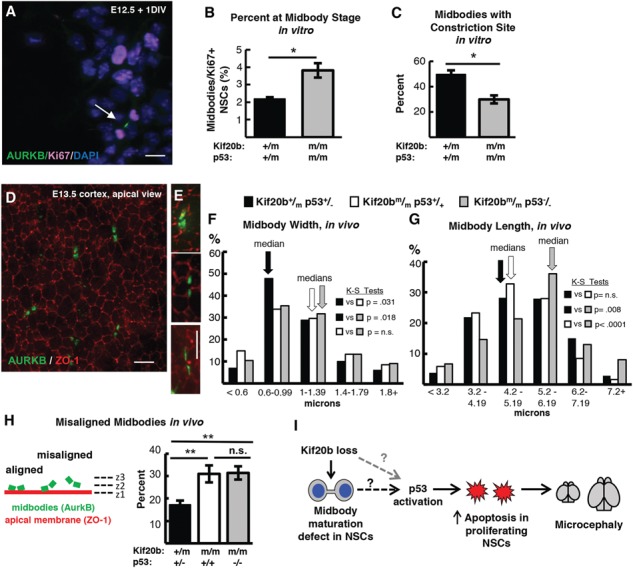
p53 deletion does not restore normal abscission of Kif20b mutant NSCs. (A) Representative image of E12.5 dissociated cortical cells, labeled with AurKB for MBs (green, arrow) and Ki67 for proliferating NSCs (pink). (B) The mean percent MB stage proliferating NSCs is significantly increased in Kif20b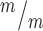 ; p53−/− cultures. n = 4 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 3 Kif20b
; p53−/− cultures. n = 4 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 3 Kif20b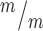 ; p53−/− coverslips; 3 embryos each, 2 litters. For comparison to Kif20b mutant cultures with wild-type p53, see Fig. S4B. (C) Of the NSCs at MB stage, the percent with a constriction site is significantly reduced in Kif20b; p53 double mutant cultures. n = 111 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 101 Kif20b
; p53−/− coverslips; 3 embryos each, 2 litters. For comparison to Kif20b mutant cultures with wild-type p53, see Fig. S4B. (C) Of the NSCs at MB stage, the percent with a constriction site is significantly reduced in Kif20b; p53 double mutant cultures. n = 111 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 101 Kif20b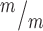 ; p53−/− MBs; 3 embryos each, 2 litters. For comparison to Kif20b
; p53−/− MBs; 3 embryos each, 2 litters. For comparison to Kif20b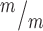 ; p53+/+ single mutant cultures, see Fig. 5E. (D) Representative image of E13.5 cortical slab, apical surface, labeled with ZO-1 (red, apical junctions) and AurKB (green, MBs). (E) NSC MBs range from short and wide (top) to long and thin (bottom). (F) The median MB width is similarly increased in Kif20b single and Kif20b;p53 double mutant cortices compared to controls. Median widths (μm) = 0.92 in Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 1.0 in Kif20b
; p53+/+ single mutant cultures, see Fig. 5E. (D) Representative image of E13.5 cortical slab, apical surface, labeled with ZO-1 (red, apical junctions) and AurKB (green, MBs). (E) NSC MBs range from short and wide (top) to long and thin (bottom). (F) The median MB width is similarly increased in Kif20b single and Kif20b;p53 double mutant cortices compared to controls. Median widths (μm) = 0.92 in Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 1.0 in Kif20b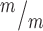 ;
p53+/+, 1.02 in Kif20b
;
p53+/+, 1.02 in Kif20b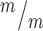 ; p53−/− cortices. (G) The median MB length is similar in Kif20b mutant and control cortices, but is significantly increased in Kif20b
; p53−/− cortices. (G) The median MB length is similar in Kif20b mutant and control cortices, but is significantly increased in Kif20b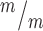 ; p53−/− cortices. Median lengths (μm) = 4.82 in Kif20b
; p53−/− cortices. Median lengths (μm) = 4.82 in Kif20b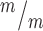 ; p53+/+, 5.11 in Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 5.43 in Kif20b
; p53+/+, 5.11 in Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 5.43 in Kif20b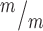 ; p53−/− cortices. n for (F, G) = 346 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 189 Kif20b
; p53−/− cortices. n for (F, G) = 346 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 189 Kif20b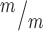 ; p53+/+ and 299 Kif20b
; p53+/+ and 299 Kif20b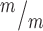 ; p53−/− MBs; 8, 5 and 7 cortical hemisphere slabs; 6, 4 and 5 embryos, 8 litters. (H) Left, Schematic of aligned and misaligned MBs of NSCS in vivo relative to the apical membrane. Right, the percent misaligned MBs is doubled in both Kif20b
; p53−/− MBs; 8, 5 and 7 cortical hemisphere slabs; 6, 4 and 5 embryos, 8 litters. (H) Left, Schematic of aligned and misaligned MBs of NSCS in vivo relative to the apical membrane. Right, the percent misaligned MBs is doubled in both Kif20b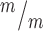 ; p53+/+ and Kif20b
; p53+/+ and Kif20b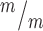 ; p53−/− cortices compared to controls. n = 8 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 7 Kif20b
; p53−/− cortices compared to controls. n = 8 Kif20b+/m; p53+/−, 7 Kif20b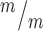 ; p53+/+, 7 Kif20b
; p53+/+, 7 Kif20b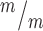 ; p53−/− cortical slabs from 6, 4, and 6 embryos, respectively, 8 litters. (I) Working model for the etiology of Kif20b microcephaly (see text also). p53 is required for NSC apoptosis and microcephaly caused by Kif20b loss but is not required for the MB defects. Thus, the MB maturation defect in the Kif20b mutant cells could signal to induce p53 accumulation through an unknown pathway (dashed black arrow with question mark). Alternatively, another cellular defect caused by Kif20b loss could induce p53 accumulation through a non-MB mediated pathway (dashed gray arrow with question mark). A–C are E12.5 cortical cultures fixed at 24 h. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test for (B, C); K.S. test for (F, G); one-way ANOVA for (H). Error bars are +/− s.e.m. Scale bars, 10 μm.
; p53−/− cortical slabs from 6, 4, and 6 embryos, respectively, 8 litters. (I) Working model for the etiology of Kif20b microcephaly (see text also). p53 is required for NSC apoptosis and microcephaly caused by Kif20b loss but is not required for the MB defects. Thus, the MB maturation defect in the Kif20b mutant cells could signal to induce p53 accumulation through an unknown pathway (dashed black arrow with question mark). Alternatively, another cellular defect caused by Kif20b loss could induce p53 accumulation through a non-MB mediated pathway (dashed gray arrow with question mark). A–C are E12.5 cortical cultures fixed at 24 h. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test for (B, C); K.S. test for (F, G); one-way ANOVA for (H). Error bars are +/− s.e.m. Scale bars, 10 μm.
