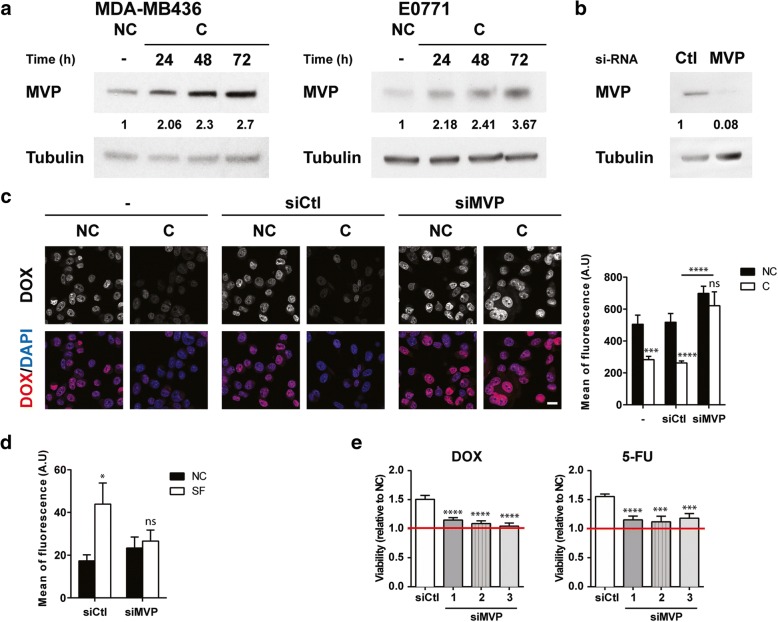
Fig. 4.
Major vault protein (MVP) is implicated in doxorubicin (DOX) efflux and mediates adipocyte-induced chemoresistance. a Immunoblots against MVP in MDA-MB436 (left panel) and E0771 (right panel) cells non-cocultivated (NC) or cocultivated (C) with adipocytes for the indicated times. Tubulin is shown as a control for equal protein loading. b MVP protein levels were analyzed after transfection of E0771 cells with Ctl and MVP small interfering RNAs (siRNA) by immunoblotting. Tubulin is shown as a control for equal protein loading. c Left panel: intracellular localization of DOX after transfection of E0771 cells with Ctl or MVP siRNAs visualized by confocal microscopy. Cells were post-incubated (C) or not (NC) with adipocytes for 24 h after DOX treatment. Nuclei were labeled with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (scale bars, 20 μm). Right panel: corresponding quantification of fluorescence intensity (DOX) in the nuclei. d Analysis of DOX content in the same number of extracellular vesicles secreted by E0771 cells transfected with siCtl or siMVP and then post-incubated (or not) with adipocyte-secreted soluble factors (SF) for 20 h. e Analysis of cytotoxicity induced by DOX or 5-FU treatments in E0771 cells transfected by siCtl or with three independent siMVP and post-incubated with adipocyte-conditioned medium (AdCM) or not (NC) for 72 h using IncuCyte technology (expressed as the ratio of surviving cells post-incubated with AdCM over surviving NC cells). Abbreviation: a.u. arbitrary units.