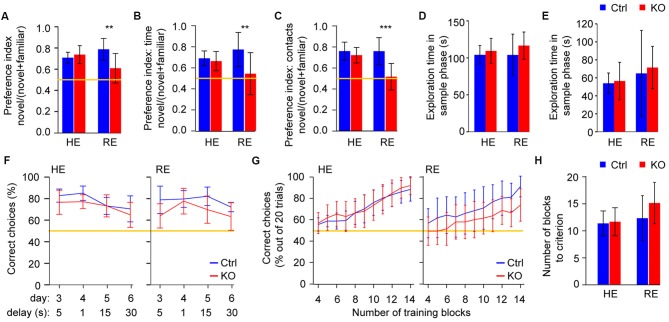
Figure 2.
Reduced environmental enrichment induces short-term memory deficits in Grin1ΔPpp1r2 animals. (A) Spatial novelty-preference (SNP) Y-maze test with average novelty preference displayed as a ratio (time in novel arm/time in both choice arms). (B,C) Novel object recognition (NOR) with preferences for novel objects displayed as ratios (interaction with novel object/interaction with both objects) calculated using either the total time of interaction (B) or the number of contacts (C). (D,E) Duration of exploration of the to-be-familiar arm during the sample trial in the SNP Y-maze test (D) and of the to-be-familiar object in the sample trial of the NOR test (E) during the sample phase of each task. (F) Rewarded alternation test of spatial working memory in HE (left) and RE (right) groups. Average performances are displayed as % of correct trials out of 10 trials conducted for each testing condition (delays and trial structure). The data represents averages across the first and the second session (conducted ca. 1 months apart) within each protocol. The first 2 days of initial training in each session are not shown. (G,H) Plus-maze assessment of appetitive long-term spatial memory. (G) Average % of correct choices made in the last 20 trials (four blocks of five trials each) in HE (left) and RE (right) groups shown across blocks 4–14, and (H) average number of training blocks required to reach the criterion (performance level of 17/20, i.e., 85% correct in four consecutive blocks). In (A–C) and (F,G) the yellow line indicates chance level performance. In all cases error bars display 95% confidence intervals. **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; simple main effects.