Fig. 5 |. circadian regulation of dopamine.
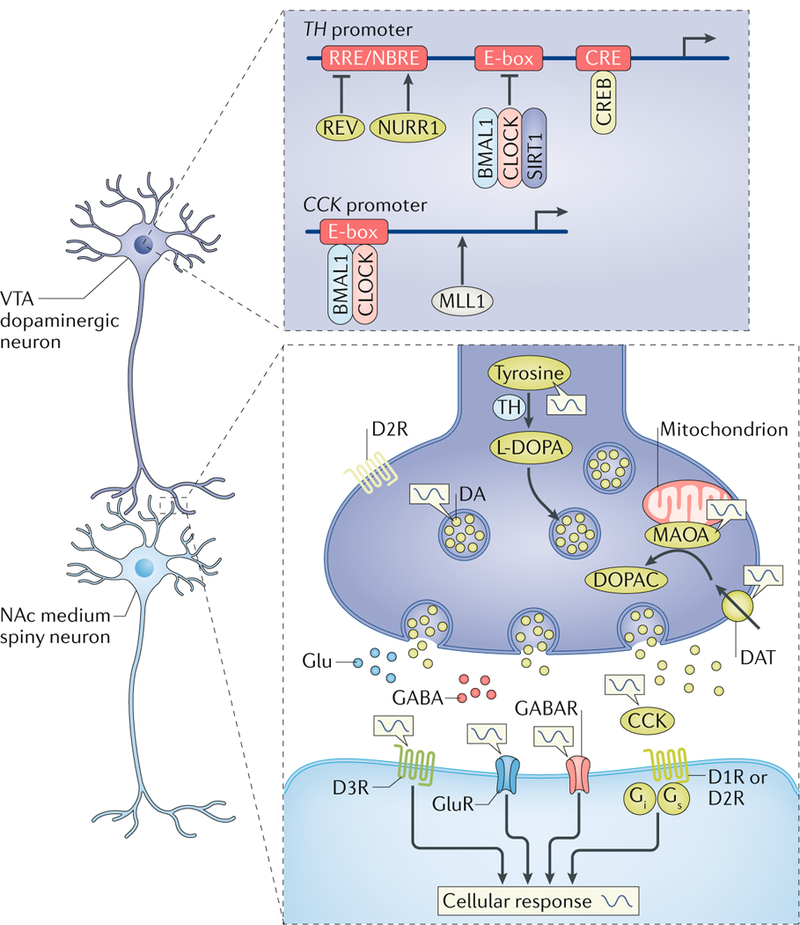
The ventral tegmental area (VTA)–nucleus accumbens (NAc) circuitry is regulated by a local molecular clock, which controls the transcription of genes involved in the dopamine (DA) signalling pathway, including those encoding: tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the major rate-limiting enzyme converting tyrosine to the DA precursor l-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA); cholecystokinin (CCK), a neuropeptide released from presynaptic DA terminals to suppress further DA release; and monoamine oxidase A (MAOA), a mitochondrial enzyme used to metabolize monoamine neurotransmitters, including DA. For example, the circadian transcription factors of circadian locomotor output cycles protein kaput (CLOCK) and brain and muscle ARNT-like 1 (BMAL1) form heterodimers and recruit the metabolic sensor and histone acetylase sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) to the enhancer box (E-box) within the TH promoter to repress transcription by cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB). CREB activates TH transcription via the CRE site, located proximal to the transcription start site and the circadian E-box. In addition, CLOCK is capable of binding the E-box within the Cck promoter to promote the transcription of Cck in the VTA. Mixed lineage leukaemia protein 1 (MLL1) is also recruited to CLOCK–BMAL1 heterodimers to promote the transcription of target genes via histone acetylation. REV-ERBα (REV) also represses transcription by binding the REV-ERB response element (RRE) promoter site in antiphase with the transcription factor NURR1 at the NURR1 binding motif, NBRE. Presynaptic dopamine 2 receptors (D2Rs) may also be regulated by the molecular clock. Diurnal rhythms of dopamine, glutamate and GABA levels, as well as of the expression and activity of their receptors, are present in the NAc, potentially temporally gating and promoting neuronal responses during certain times of day. DAT, DA transporter; DOPAC, 3–4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid; GABAR, GABA receptor; Glu, glutamate; GluR, glutamate receptor (ionotropic).
