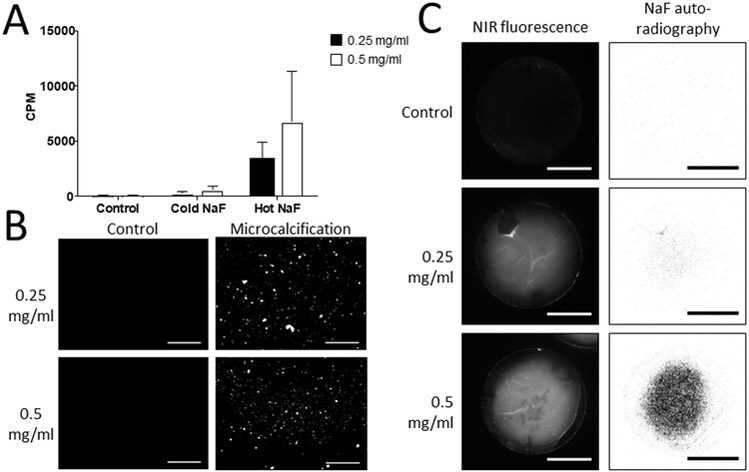
Figure 2. Collagen hydrogels demonstrate affinity of 18F-fluoride for microcalcifications.
A, Quantification of radioactive signal of 18F-NaF bound to microcalcifications within collagen hydrogels of two different collagen concentrations and two-way ANOVA analysis. Control – collagen hydrogels incubated without extracellular vesicles (0.25 mg/ml - 0.88×102±0.02×102 CPM; 0.5 mg/ml - 0.85×102±0.04 ×102 CPM). Cold NaF - a mixture of radioactively labeled 18F-fluoride and unlabeled fluoride to test for nonspecific binding of the tracer to microcalcifications (0.25 mg/ml - 2.59×102±1.62×102 CPM; 0.5 mg/ml - 5.67×102±2.79×102 CPM). Hot NaF – radioactively labeled 18F-fluoride for total binding (0.25 mg/ml - 33.8×102±12.4×102 CPM; 0.5 mg/ml - 67.7×102±37.4×102 CPM) (p=0.0014). P-value of the labeling method = 0.0014, p-value associated with collagen concentration = 0.2119, p-value of the interaction = 0.2956. B, Fluorescence microscopy of microcalcifications in collagen hydrogels with microcalcifications after incubation with bisphosphonate-based fluorescent tracer (scale bars 100 µm). Two different collagen concentrations were used for the hydrogels. C, NIRF and autoradiography of microcalcifications in 3D collagen hydrogels after incubation with a NIRF tracer or 18F-fluoride, respectively (scale bars 10 mm).