Fig. 1:
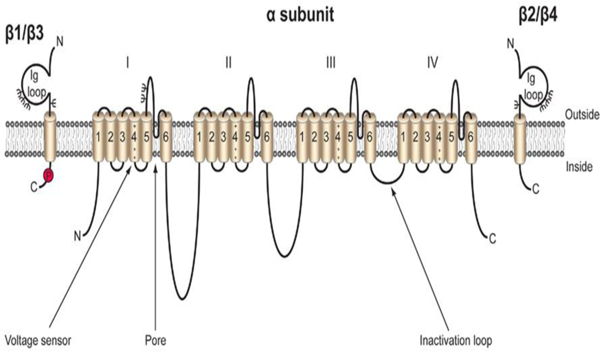
Cartoon diagram of the VGSC. VGSCs are comprised of one pore-forming, or α subunit, and one or two non-pore forming β subunits. The α subunit is made up four domains each of which contain six transmembrane segments. The voltage sensor is located in transmembrane segment four of each domain (Catterall). There are five β subunits, β1-β4, and the developmentally regulated β1B. β1-β4 all contain an intracellular C-terminal domain, a single transmembrane domain, and a large extracellular immunoglobulin (Ig) domain (Isom et al. 1994). β1B also possesses an Ig domain, but does not contain an intracellular or transmembrane domain, resulting in a soluble, secreted protein (Patino et al. 2011). β1 and β3 are non-covalently linked to the α subunit, while β2 and β4 are linked by disulfide bonds. Each β subunit is heavily glycosylated, denoted by Ψ, and β1 also contains an intracellular phosphorylation site at tyrosine 181 (Isom and Catterall 1996; Malhotra et al. 2004). Figure reproduced from (Brackenbury and Isom 2011).
