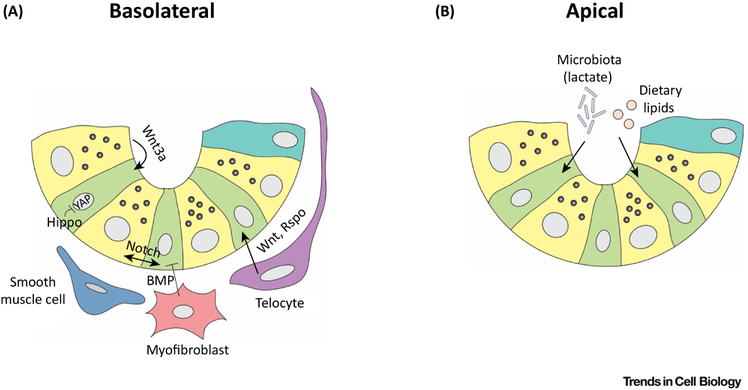
Figure 3: Canonical pathways present in the ISC niche.
Different niche factors impact the activity of active intestinal stem cells (ISCs) during homeostasis. (A) From the basolateral side, the integrity and function of ISCs is maintained directly or indirectly by “homeostatic niche” factors such as Wnts, R-spondins (Rspo), BMP and Hedgehog, secreted by stromal populations such as telocytes, myofibroblasts and smooth muscle cells; and Notch and redundant Wnt signals secreted by epithelial Paneth cells. The Hippo pathway via YAP may transduce mechanosensory signals. (B) On the apical side, dietary lipids impact directly the activity of ISCs and commensal microbiota contribute to the “homeostatic niche” by producing beneficial signals such as lactate.